Optimising the photothrombotic model of stroke in the C57BI/6 and FVB/N strains of mouse
- PMID: 35534531
- PMCID: PMC9085761
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-11793-6
Optimising the photothrombotic model of stroke in the C57BI/6 and FVB/N strains of mouse
Abstract
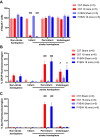
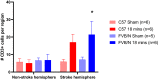
The photothrombotic stroke model relies on the interaction between photosensitive-dye and light for clot formation. Interestingly, the relationship between the length of light exposure and stroke-outcome has never been examined. This model has yet to be established in the FVB/N strain, even though stroke-outcomes are strain-specific. Therefore, this study aimed to examine the effect of different lengths of light exposure in two strains of mice on photothrombotic stroke. Male FVB/N and C57Bl/6 mice were subjected to stroke using 15, 18, or 20-min light exposure. Mice underwent functional testing for up to 7 days. Infarct volume was assessed with thionin staining, and cellular responses to injury analysed via immunofluorescence at 7-days post-stroke. Blood brain barrier (BBB) breakdown was assessed using Evans blue dye at 4.5-h post-stroke. Increasing light exposure from 15 to 20-min increased infarct volume but not functional deficit. Interestingly, there were strain-specific differences in functional outcomes, with FVB/N mice having less deficit on the hanging wire test than C57BI/6 after 15-min of light exposure. The opposite was seen in the adhesive removal test. There was no difference in the number of neurons, astrocytes, microglia, macrophages, and T cells between the strains, despite FVB/N mice demonstrating greater BBB breakdown and an enlarged spleen post-stroke. Increasing light exposure systematically increases infarct volume but does not worsen functional outcomes. FVB/N and C57Bl/6 mice exhibit subtle differences in functional outcomes post stroke, which highlights the need to choose tests which are appropriate for the mouse strain being used.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

