The disordered N-terminal domain of DNMT3A recognizes H2AK119ub and is required for postnatal development
- PMID: 35534561
- PMCID: PMC9295050
- DOI: 10.1038/s41588-022-01063-6
The disordered N-terminal domain of DNMT3A recognizes H2AK119ub and is required for postnatal development
Abstract
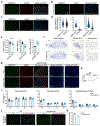
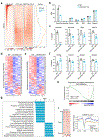
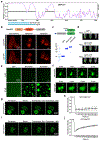
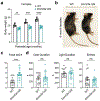
DNA methyltransferase 3a (DNMT3A) plays a crucial role during mammalian development. Two isoforms of DNMT3A are differentially expressed from stem cells to somatic tissues, but their individual functions remain largely uncharacterized. Here we report that the long isoform DNMT3A1, but not the short DNMT3A2, is essential for mouse postnatal development. DNMT3A1 binds to and regulates bivalent neurodevelopmental genes in the brain. Strikingly, Dnmt3a1 knockout perinatal lethality could be partially rescued by DNMT3A1 restoration in the nervous system. We further show that the intrinsically disordered N terminus of DNMT3A1 is required for normal development and DNA methylation at DNMT3A1-enriched regions. Mechanistically, a ubiquitin-interacting motif embedded in a putative α-helix within the N terminus binds to mono-ubiquitinated histone H2AK119, probably mediating recruitment of DNMT3A1 to Polycomb-regulated regions. These data demonstrate an isoform-specific role for DNMT3A1 in mouse postnatal development and reveal the N terminus as a necessary regulatory domain for DNMT3A1 chromatin occupancy and functions in the nervous system.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature America, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


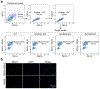


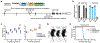

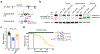
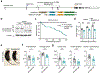



Comment in
-
DNMT3A binds ubiquitinated histones to regulate bivalent genes.Nat Genet. 2022 May;54(5):537-538. doi: 10.1038/s41588-022-01073-4. Nat Genet. 2022. PMID: 35534560 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Smith ZD & Meissner A DNA methylation: Roles in mammalian development. Nat. Rev. Genet 14, 204–220 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Greenberg MVC & Bourc’his D The diverse roles of DNA methylation in mammalian development and disease. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol 20, 590–607 (2019). - PubMed
-
- Okano M, Bell DW, Haber DA & Li E DNA methyltransferases Dnmt3a and Dnmt3b are essential for de novo methylation and mammalian development. Cell 99, 247–257 (1999). - PubMed
-
- Nguyen S, Meletis K, Fu D, Jhaveri S & Jaenisch R Ablation of de novo DNA methyltransferase Dnmt3a in the nervous system leads to neuromuscular defects and shortened lifespan. Dev. Dyn 236, 1663–1676 (2007). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

