Epigenetic, genetic and maternal effects enable stable centromere inheritance
- PMID: 35534577
- PMCID: PMC9107508
- DOI: 10.1038/s41556-022-00897-w
Epigenetic, genetic and maternal effects enable stable centromere inheritance
Abstract
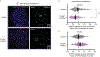
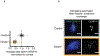
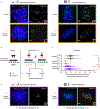
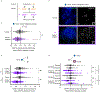
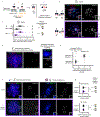
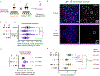
Centromeres are defined epigenetically by the histone H3 variant CENP-A. The propagation cycle by which pre-existing CENP-A nucleosomes serve as templates for nascent assembly predicts the epigenetic memory of weakened centromeres. Using a mouse model with reduced levels of CENP-A nucleosomes, we find that an embryonic plastic phase precedes epigenetic memory through development. During this phase, nascent CENP-A nucleosome assembly depends on the maternal Cenpa genotype rather than the pre-existing template. Weakened centromeres are thus limited to a single generation, and parental epigenetic differences are eliminated by equal assembly on maternal and paternal centromeres. These differences persist, however, when the underlying DNA of parental centromeres differs in repeat abundance, as assembly during the plastic phase also depends on sufficient repetitive centromere DNA. With contributions of centromere DNA and the Cenpa maternal effect, we propose that centromere inheritance naturally minimizes fitness costs associated with weakened centromeres or epigenetic differences between parents.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interest declaration
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
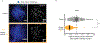
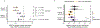

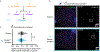
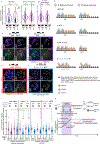
References
-
- Dumont M & Fachinetti D DNA Sequences in Centromere Formation and Function. Prog Mol Subcell Biol 56 305–336 (2017). - PubMed
-
- Chmátal L, Schultz RM, Black BE & Lampson MA Cell Biology of Cheating-Transmission of Centromeres and Other Selfish Elements Through Asymmetric Meiosis. Prog Mol Subcell Biol 56 377–396 (2017). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

