The HMCES DNA-protein cross-link functions as an intermediate in DNA interstrand cross-link repair
- PMID: 35534579
- PMCID: PMC9949344
- DOI: 10.1038/s41594-022-00764-0
The HMCES DNA-protein cross-link functions as an intermediate in DNA interstrand cross-link repair
Abstract
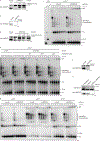
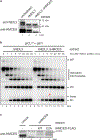
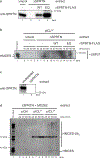
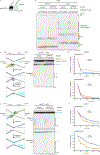
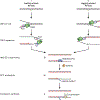
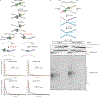
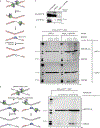
The 5-hydroxymethylcytosine binding, embryonic stem-cell-specific (HMCES) protein forms a covalent DNA-protein cross-link (DPC) with abasic (AP) sites in single-stranded DNA, and the resulting HMCES-DPC is thought to suppress double-strand break formation in S phase. However, the dynamics of HMCES cross-linking and whether any DNA repair pathways normally include an HMCES-DPC intermediate remain unknown. Here, we use Xenopus egg extracts to show that an HMCES-DPC forms on the AP site generated during replication-coupled DNA interstrand cross-link repair. We show that HMCES cross-links form on DNA after the replicative CDC45-MCM2-7-GINS (CMG) helicase has passed over the AP site, and that HMCES is subsequently removed by the SPRTN protease. The HMCES-DPC suppresses double-strand break formation, slows translesion synthesis past the AP site and introduces a bias for insertion of deoxyguanosine opposite the AP site. These data demonstrate that HMCES-DPCs form as intermediates in replication-coupled repair, and they suggest a general model of how HMCES protects AP sites during DNA replication.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature America, Inc.
Figures







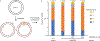

References
-
- Lindahl T. Instability and decay of the primary structure of DNA. Nature 362, 709–15 (1993). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

