Jejunogastric intussusception after pancreaticoduodenectomy: a case report
- PMID: 35534691
- PMCID: PMC9086021
- DOI: 10.1186/s40792-022-01424-7
Jejunogastric intussusception after pancreaticoduodenectomy: a case report
Abstract
Background: Jejunogastric intussusception (JGI) is a rare, but potentially fatal complication that can occur following gastric surgery, and the reported incidence of JGI is as low as 0.1%. Early diagnosis and treatment are critical for JGI to prevent major complications such as bowel necrosis and death. Although emergency surgery is the standard treatment, endoscopic reduction has also been reported to be effective in JGI patients without bowel necrosis. Several early recurrent cases treated with surgical or endoscopic reduction have been reported. We report an extremely rare case of JGI after pancreaticoduodenectomy (PD) using Child's procedure that was successfully treated with surgical reduction and fixation.
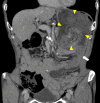
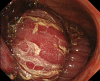
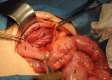
Case presentation: An 81-year-old man who had undergone PD using Child's procedure 3 years ago presented to our hospital with epigastric pain and nausea. His vital signs were stable, and abdominal examination revealed mild tenderness with a palpable mass in the mid-epigastrium. Abdominal computed tomography (CT) and gastroscopy revealed a JGI of the efferent loop, and exploratory laparotomy was immediately performed. During the operation, the efferent loop showed no adhesions and was intussuscepted through the gastrojejunostomy into the gastric lumen. An incision in the anterior wall of the stomach revealed no evidence of ischemia of the intussusceptum. The efferent loop was reduced using Hutchinson's maneuver and fixed to the afferent loop to prevent a recurrence. The postoperative course was uneventful, and there was no sign of recurrence 12 months postoperatively.
Conclusions: JGI after PD is an extremely rare, but has severe complications. Surgery might be the optimal treatment for JGI in terms of preventing recurrence, even in cases without bowel necrosis.
Keywords: Child’s procedure; Complication; Intussusception; Pancreaticoduodenectomy.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest for this article
Figures
Similar articles
-
Jejunogastric intussusception after Whipple procedure with B-II reconstruction: a case report.BMC Gastroenterol. 2020 Apr 10;20(1):101. doi: 10.1186/s12876-020-01259-2. BMC Gastroenterol. 2020. PMID: 32276605 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Jejunogastric intussusception after totally laparoscopic distal gastrectomy for gastric cancer: a rare case report and review of the literature.Korean J Clin Oncol. 2022 Jun;18(1):56-59. doi: 10.14216/kjco.22007. Epub 2022 Jun 30. Korean J Clin Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36945333 Free PMC article.
-
Jejunogastric intussusception: a rare complication of gastric cancer surgery.Int J Clin Exp Med. 2014 Nov 15;7(11):4498-502. eCollection 2014. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2014. PMID: 25550976 Free PMC article.
-
Jejunogastric intussusception associated with jejunojejunal intussusception (double telescoping) occurring 20 years after gastrojejunostomy.Int J Emerg Med. 2024 Mar 11;17(1):38. doi: 10.1186/s12245-024-00612-6. Int J Emerg Med. 2024. PMID: 38462623 Free PMC article.
-
Retrograde jejunogastric intussusception: A case report and review of the literature.Asian J Surg. 2017 Jul;40(4):309-312. doi: 10.1016/j.asjsur.2014.04.001. Epub 2014 Jun 14. Asian J Surg. 2017. PMID: 24938859 Review.
Cited by
-
Intussusception of Gastrojejunostomy After Pancreatoduodenectomy With Billroth II Reconstruction.Cureus. 2024 Jan 8;16(1):e51880. doi: 10.7759/cureus.51880. eCollection 2024 Jan. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38327972 Free PMC article.
-
Intussusception following diaphragmatic rupture surgery: A rare case.Int J Surg Case Rep. 2023 Nov;112:108953. doi: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2023.108953. Epub 2023 Oct 17. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2023. PMID: 37856974 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

