Radiographic and clinical outcome of tibial plateau fractures treated with bone allograft
- PMID: 35534713
- PMCID: PMC9085366
- DOI: 10.1007/s00402-022-04461-x
Radiographic and clinical outcome of tibial plateau fractures treated with bone allograft
Abstract
Background: To determine the clinical outcome of patients who had been treated with bone allografts during open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF) of tibial head fractures.
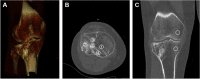
Methods: Patients who suffered a medial, lateral, or bicondylar fracture of the tibial plateau and underwent surgical treatment by open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF) using human femoral head bone allografts were included. Patients were invited to provide information for the following: Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index (WOMAC), EuroQol Five Dimension score (EQ-5D), Lower Extremity Functional Scale (LEFS) and Parker Mobility Score. Bone mineral density (BMD) of the allograft area and the healthy human bone tissue were measured by quantitative computed tomography.
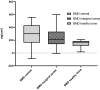
Results: A total of 22 patients with a mean follow-up time of 2.88 ± 2.46 years were included in our study. The most common fractures observed in this study were classified as Schatzker II (11 patients, 50.0%) or AO/OTA 41.B3 (12 patients, 54.5%) fractures. Postoperative WOMAC total was 13.0 (IQR = 16.3, range 0-33). Median quality of life (EQ-5D) score was 0.887 ± 0.121 (range 0.361-1.000). Median Lower Extremity Functional Scale (LEFS) score was 57.5 ± 19.0 (range 33-79). Mean Parker Mobility Score was 9 (range 6-9). Median bone mineral density (BMD) for the whole group was 300.04 ± 226.02 mg/cm3 (range - 88.68 to 555.06 mg/cm3) for region of interest (ROI 5) (central), 214.80 ± 167.45 mg/cm3 (range - 7.16 to 597.21 mg/cm3) for ROI 1-4 (marginal zones: medial, lateral, ventral, dorsal) and 168.14 ± 65.54 mg/cm3 (range 17.47-208.97 mg/cm3) for healthy bone tissue (femur and tibia).
Conclusion: Based on WOMAC scores, LEFS, ambulatory status, and quality of life findings, it can be concluded that following tibial head ORIF with allograft bone patients has promising results.
Keywords: Bone allograft; Bone graft; Bone mineral density; Quantitative computed tomography; Tibial plateau fractures.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. The authors alone are responsible for the content and writing of the article.
Figures
References
-
- Bagherifard A, Ghandhari H, Jabalameli M, Rahbar M, Hadi H, Moayedfar M, Sajadi MM, Karimpour A. Autograft versus allograft reconstruction of acute tibial plateau fractures: a comparative study of complications and outcome. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2017;27(5):665–671. doi: 10.1007/s00590-016-1863-y. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hofmann A, Gorbulev S, Guehring T, Schulz AP, Schupfner R, Raschke M, Huber-Wagner S, Rommens PM. Autologous iliac bone graft compared with biphasic hydroxyapatite and calcium sulfate cement for the treatment of bone defects in tibial plateau fractures: a prospective, randomized, open-label, multicenter study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2020;102(3):179–193. doi: 10.2106/jbjs.19.00680. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

