Identification of miRNA-mRNA-TF regulatory networks in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of type 1 diabetes
- PMID: 35534828
- PMCID: PMC9087960
- DOI: 10.1186/s12902-022-01038-y
Identification of miRNA-mRNA-TF regulatory networks in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of type 1 diabetes
Abstract
Background: Type 1 diabetes (T1D) is a T lymphocyte-mediated and B lymphocyte-assisted autoimmune disease. We aimed to identify abnormally expressed genes in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) of T1D and explore their possible molecular regulatory network.
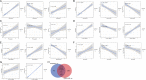
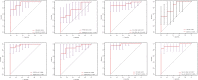
Methods: Expression datasets were downloaded from the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database. Then, the differentially expressed genes (DEGs) and differentially expressed miRNAs (DEmiRNAs) were identified, and functional enrichment and immune cell infiltration analysis were performed. The starBase, miRTarBase, TarBase, JASPAR, ENCODE, and TRRUST databases constructed the miRNA-mRNA-TF regulatory network. The ROC curves were plotted to evaluate the sensitivity and specificity of miRNAs and mRNAs.
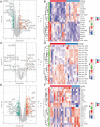
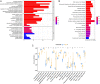
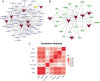
Result: A total of 216 DEGs directly or indirectly related to type I diabetes mellitus, natural killer cell-mediated cytotoxicity, Th1, and Th2 cell differentiation, and the IL-17 and TNF signaling pathways were obtained. The miRNA-mRNA-TF network indicates that miR-320a and SOX5 are the only miRNAs and TFs that both target ADM and RRAGD. The ROC curves showed that ADM (0.9375), RRAGD (0.8958), and hsa-mir-320a (0.9417) had high accuracy in T1D diagnosis.
Conclusion: The constructed regulatory networks, including miR-320a/ADM/SOX5 and miR-320a/RRAGD/SOX5, may provide new insight into the mechanisms of development and progression in T1D.
Keywords: Differentially expressed genes (DEGs); MicroRNAs; Regulatory networks; Transcription factors (TFs); Type 1 diabetes (T1D).
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

