High-flow nasal cannula versus standard low-flow nasal cannula during deep sedation in patients undergoing radiofrequency atrial fibrillation catheter ablation: a single-centre randomised controlled trial
- PMID: 35534903
- PMCID: PMC9082831
- DOI: 10.1186/s13063-022-06362-1
High-flow nasal cannula versus standard low-flow nasal cannula during deep sedation in patients undergoing radiofrequency atrial fibrillation catheter ablation: a single-centre randomised controlled trial
Abstract
Background: To our knowledge, there are few trials studying the effect of high-flow nasal cannula (HFNC) during deep sedation. Our hypothesis is that high-flow nasal cannula (HFNC) will prevent hypoxemia and desaturation as compared to low-flow nasal cannula (LFNC) during prolonged deep sedation in patients with atrial fibrillation undergoing radiofrequency catheter ablation (RFCA).
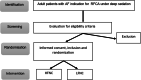
Methods: A single-centre, randomised controlled trial with HFNC as the intervention and LFNC as the control group. A total of 94 adult patients per group undergoing elective radiofrequency atrial fibrillation catheter ablation under deep sedation. will be included. The primary outcome is the lowest oxygen saturation (SpO2). Secondary outcomes are as follows: the duration of lowest SpO2, cross over from oxygen therapy in both directions, incidence of SpO2 below 90% > 60 seconds, adverse sedation events, adverse effects of HFNC, mean CO2, peak CO2 and patients experience with oxygen therapy. The study will take place during the 2-day admission period for RFCA. Patients can fill out their questionnaires in the first week after treatment.
Discussion: HFNC is increasingly used as a technique for oxygen delivery in procedural sedation and analgesia. We hypothesise that HFNC is superior to the standard treatment LFNC in patients under deep sedation with respect to the incidence of desaturation. To our knowledge, there are no adequately powered clinical trial studies on the effects of HFNC in prolonged deep sedation.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT04842253. Registered on 04 April 2021.
Keywords: Anaesthesiology; Atrial fibrillation; Deep sedation; High-flow nasal cannula; Radiofrequency catheter ablation; Randomised controlled trial; Sedation.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Incidence of oxygen desaturation using a high-flow nasal cannula versus a facemask during flexible bronchoscopy in patients at risk of hypoxemia: a randomised controlled trial.BMC Pulm Med. 2022 Oct 27;22(1):389. doi: 10.1186/s12890-022-02188-4. BMC Pulm Med. 2022. PMID: 36303179 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
High-flow versus standard nasal cannula in morbidly obese patients during colonoscopy: A prospective, randomized clinical trial.J Clin Anesth. 2019 May;54:19-24. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinane.2018.10.026. Epub 2018 Nov 2. J Clin Anesth. 2019. PMID: 30391445 Clinical Trial.
-
Optimal flow of high-flow nasal cannula oxygenation to prevent desaturation during sedation for bronchoscopy: a randomized controlled study.Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2024 Jan-Dec;18:17534666241246637. doi: 10.1177/17534666241246637. Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2024. PMID: 38659187 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Meta-analysis comparing the efficiency of high-flow nasal cannula versus low-flow nasal cannula in patients undergoing endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography.Proc (Bayl Univ Med Cent). 2022 Apr 20;35(4):485-491. doi: 10.1080/08998280.2022.2062554. eCollection 2022. Proc (Bayl Univ Med Cent). 2022. PMID: 35754579 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High-flow versus conventional nasal cannula oxygen supplementation therapy and risk of hypoxia in gastrointestinal endoscopies: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Expert Rev Respir Med. 2022 Mar;16(3):323-332. doi: 10.1080/17476348.2022.2042256. Epub 2022 Feb 22. Expert Rev Respir Med. 2022. PMID: 35157538
Cited by
-
Effect of inspiratory muscle training on hypoxemia in obese patients undergoing painless gastroscopy: protocol for a single-center, double-blind, randomized controlled trial.Front Med (Lausanne). 2023 Sep 14;10:1269486. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1269486. eCollection 2023. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37790126 Free PMC article.
-
Use of high flow nasal cannula in critical burn patient during deep sedation in enzymatic bromelain debridement (nexobrid®): a single center brief report.Ann Burns Fire Disasters. 2024 Dec 31;37(4):294-299. eCollection 2024 Dec. Ann Burns Fire Disasters. 2024. PMID: 39741773 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous