Scalable manufacturing of clinical-grade differentiated cardiomyocytes derived from human-induced pluripotent stem cells for regenerative therapy
- PMID: 35534945
- PMCID: PMC9357358
- DOI: 10.1111/cpr.13248
Scalable manufacturing of clinical-grade differentiated cardiomyocytes derived from human-induced pluripotent stem cells for regenerative therapy
Abstract
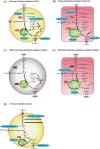
Basic research on human pluripotent stem cell (hPSC)-derived cardiomyocytes (CMs) for cardiac regenerative therapy is one of the most active and complex fields to achieve this alternative to heart transplantation and requires the integration of medicine, science, and engineering. Mortality in patients with heart failure remains high worldwide. Although heart transplantation is the sole strategy for treating severe heart failure, the number of donors is limited. Therefore, hPSC-derived CM (hPSC-CM) transplantation is expected to replace heart transplantation. To achieve this goal, for basic research, various issues should be considered, including how to induce hPSC proliferation efficiently for cardiac differentiation, induce hPSC-CMs, eliminate residual undifferentiated hPSCs and non-CMs, and assess for the presence of residual undifferentiated hPSCs in vitro and in vivo. In this review, we discuss the current stage of resolving these issues and future directions for realizing hPSC-based cardiac regenerative therapy.
© 2022 The Authors. Cell Proliferation published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
K.F. is a CEO of Heartseed, Inc. S.T. is an advisor of Heartseed, Inc. S.T. and K.F. own equity in Heartseed, Inc. The remaining authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Tohyama S, Hattori F, Sano M, et al. Distinct metabolic flow enables large‐scale purification of mouse and human pluripotent stem cell‐derived cardiomyocytes. Cell Stem Cell. 2013;12(1):127‐137. - PubMed
-
- Tohyama S, Fujita J, Hishiki T, et al. Glutamine oxidation is indispensable for survival of human pluripotent stem cells. Cell Metab. 2016;23(4):663‐674. - PubMed
-
- Ben‐David U, Gan QF, Golan‐Lev T, et al. Selective elimination of human pluripotent stem cells by an oleate synthesis inhibitor discovered in a high‐throughput screen. Cell Stem Cell. 2013;12(2):167‐179. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

