PET/CT in congenital hyperinsulinism: transforming patient's lives by molecular hybrid imaging
- PMID: 35535120
- PMCID: PMC9077170
PET/CT in congenital hyperinsulinism: transforming patient's lives by molecular hybrid imaging
Abstract
Congenital hyperinsulinism (HI) is a life-threatening condition characterized by severe and recurrent episodes of hypoglycaemia due to defects in key genes involved in regulating insulin secretion. The delay in diagnosis and inappropriate management of HI lead to high risk of permanent hypoglycemic brain injury. The management of HI is challenging as each form of HI (focal, diffuse, and atypical) requires its own therapeutic strategy. In HI diagnostic work-up, integrated PET/CT scan is currently the first-line imaging technique allowing to differentiate between diffuse and focal form and, in the latter case, to localize the focus within the pancreas with high precision. Only in focal HI partial pancreatectomy is the treatment of choice and a curative surgical treatment means a real chance of transforming patient's lives and HI patient's future. The aim of this review is to discuss the role of PET/CT imaging in HI scenario, its technical advantages and limitations and how successful surgery is strongly dependent on accurate preoperative assessment (genetic analysis and PET/CT scan). A multidisciplinary approach in HI diagnosis and treatment inside a single team (involving different expertise) allows to manage children safely and properly, supporting their families in an organized care network.
Keywords: Congenital hyperinsulinism; DOPA; PET/CT; molecular hybrid imaging; pediatric.
AJNMMI Copyright © 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures

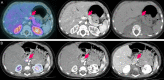
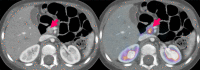
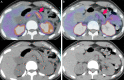
References
-
- States LJ, Saade-Lemus S, De Leon DD. 18F-L 3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine PET/computed tomography in the management of congenital hyperinsulinism. PET Clin. 2020;15:349–359. - PubMed
-
- Bruining GJ. Recent advances in hyperinsulinism and the pathogenesis of diabetes mellitus. Curr Opin Pediatr. 1990;2:758–765.
-
- Han B, Mohamed Z, Estebanez MS, Craigie RJ, Newbould M, Cheesman E, Padidela R, Skae M, Johnson M, Flanagan S, Ellard S, Cosgrove KE, Banerjee I, Dunne MJ. Atypical forms of congenital hyperinsulinism in infancy are associated with mosaic patterns of immature islet cells. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2017;102:3261–3267. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sempoux C, Capito C, Bellanné-Chantelot C, Verkarre V, de Lonlay P, Aigrain Y, Fekete C, Guiot Y, Rahier J. Morphological mosaicism of the pancreatic islets: a novel anatomopathological form of persistent hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia of infancy. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2011;96:3785–3793. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
