Identification of 1,2,4-Oxadiazoles-Based Novel EGFR Inhibitors: Molecular Dynamics Simulation-Guided Identification and in vitro ADME Studies
- PMID: 35535170
- PMCID: PMC9077134
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S357765
Identification of 1,2,4-Oxadiazoles-Based Novel EGFR Inhibitors: Molecular Dynamics Simulation-Guided Identification and in vitro ADME Studies
Abstract
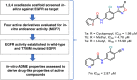
Background: In this work, we have identified heterocyclic derivatives with 1,2,4 oxadiazole scaffold mimicking the functions of tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Fourteen molecules that displayed the best fit were picked from the library of compounds and studied under in-silico and in-vitro conditions. Four compounds were selected for further cytotoxicity and ADME (Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, Elimination) profiling showing IC50 (from 8-13 µM) values against EGFR positive cancer cell line (MCF7).
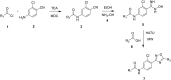
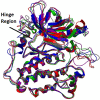
Methods: A molecular dynamics simulation study was performed to understand the correlation of non-covalent binding energies with biological activity. The drug-like properties of the selected four compounds (7a, 7b, 7e, and 7m) were evaluated by in-vitro ADME studies. Compounds 7a, 7b, and 7m were the active compounds in the molecular dynamics simulations study. Further, EGFR binding activity was confirmed with EGFRWT and EGFRT790M kinase assay using a luminescence-based method.
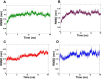
Results: These compounds (7a, 7b, and 7m) showed activity against EGFRWT and mutant EGFRT790M, exhibiting IC50 values of <10 and <50 micromolar, respectively. These compounds also possess moderate aqueous solubility in 40-70 µg/mL at pH 7.4 and 30-100 µg/mL at pH 4.0. Further, 7a, 7b, and 7m showed balanced lipophilicity with Log D values ranging from 1-3. They demonstrated a good correlation in Caco-2 permeability with Apparent permeability (Papp) 1 to 5 × 10-6 cm/s in comparison with 7e, which was found to be highly lipophilic (Log D >5) and showed high permeability (Papp 17 × 10-6 cm/s). Lastly, all these compounds were moderately stable in liver microsomes at alkaline pH with a half-life of 30-60 min, while at a highly acidic pH (2.0), the compounds were stable up to 15-20 min.
Conclusion: Overall, in-vitro ADME results of these molecules showed good drug-like properties, which are well correlated with the in-silico ADME data, making them ideal for developing an oral drug delivery formulation.
Keywords: 1,2,4-oxadiazoles; absorption; anticancer; distribution; excretion; metabolism; molecular dynamics; structure-based design.
© 2022 Unadkat et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Vishal Unadkat and Shishir Rohit are employees of Kashiv Biosciences Pvt Ltd, Ahmedabad 382210, Gujarat, India. Vinod Sanna is an employee of Piramal Pharma Solutions, Ahmedabad, 382213, Gujarat, India. The authors report no other potential conflicts of interest for this work.
Figures

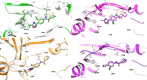



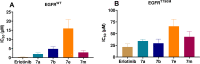
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

