Novel Liposomal Rolipram Formulation for Clinical Application to Reduce Emesis
- PMID: 35535222
- PMCID: PMC9078351
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S355796
Novel Liposomal Rolipram Formulation for Clinical Application to Reduce Emesis
Abstract
Introduction: The phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE4) inhibitor, rolipram, has beneficial effects on tissue inflammation, injury and fibrosis, including in the liver. Since rolipram elicits significant CNS side-effects in humans (ie, nausea and emesis), our group developed a fusogenic lipid vesicle (FLV) drug delivery system that targets the liver to avoid adverse events. We evaluated whether this novel liposomal rolipram formulation reduces emesis.
Methods: C57Bl/6J male mice were used to compare the effect of three doses of free and FLV-delivered (FLVs-Rol) rolipram in a behavioral correlate model of rolipram-induced emesis. Tissue rolipram and rolipram metabolite levels were measured using LC-MS/MS. The effect of FLVs-Rol on brain and liver PDE4 activities was evaluated.
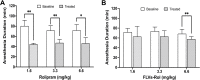
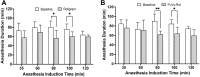
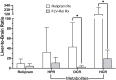
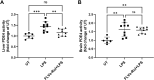
Results: Low and moderate doses of free rolipram significantly reduced anesthesia duration, while the same doses of FLVs-Rol had no effect. However, the onset and duration of adverse effects (shortening of anesthesia period) elicited by a high dose of rolipram was not ameliorated by FLVs-Rol. Post-mortem analysis of brain and liver tissues demonstrated that FLVs affected the rate of rolipram uptake by liver and brain. Lastly, administration of a moderate dose of FLVs-Rol attenuated endotoxin induced PDE4 activity in the liver with negligible effect on the brain.
Discussion: The findings that the low and moderate doses of FLVs-Rol did not shorten the anesthesia duration time suggest that FLV delivery prevented critical levels of drug from crossing the blood-brain barrier (BBB) to elicit CNS side-effects. However, the inability of high dose FLVs-Rol to prevent CNS side-effects indicates that there was sufficient unencapsulated rolipram to cross the BBB and shorten anesthesia duration. Notably, a moderate dose of FLVs-Rol was able to decrease PDE4 activity in the liver without affecting the brain. Taken together, FLVs-Rol has a strong potential for clinical application for the treatment of liver disease without side effects.
Keywords: PDE4; liposomes; liver; rolipram; side-effects.
© 2022 Gobejishvili et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Drs. Maldonado and Bauer declare a conflict of interest in employment and having equity in EndoProtech, Inc. The authors report no other conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Attenuation of ethanol abstinence-induced anxiety- and depressive-like behavior by the phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor rolipram in rodents.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2017 Oct;234(20):3143-3151. doi: 10.1007/s00213-017-4697-3. Epub 2017 Jul 27. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2017. PMID: 28748375
-
PAN-selective inhibition of cAMP-phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE4) induces gastroparesis in mice.FASEB J. 2020 Sep;34(9):12533-12548. doi: 10.1096/fj.202001016RR. Epub 2020 Aug 1. FASEB J. 2020. PMID: 32738081 Free PMC article.
-
The PDE4 inhibitor roflumilast improves memory in rodents at non-emetic doses.Behav Brain Res. 2016 Apr 15;303:26-33. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2016.01.031. Epub 2016 Jan 18. Behav Brain Res. 2016. PMID: 26794595
-
PET measurements of cAMP-mediated phosphodiesterase-4 with (R)-[11C]rolipram.Curr Radiopharm. 2011 Jan;4(1):44-58. doi: 10.2174/1874471011104010044. Curr Radiopharm. 2011. PMID: 22191614 Review.
-
Proposal for pharmacologically distinct conformers of PDE4 cyclic AMP phosphodiesterases.Cell Signal. 1997 May-Jun;9(3-4):227-36. doi: 10.1016/s0898-6568(96)00173-8. Cell Signal. 1997. PMID: 9218122 Review.
Cited by
-
Increased expression of phosphodiesterase 4 in activated hepatic stellate cells promotes cytoskeleton remodeling and cell migration.J Pathol. 2023 Nov;261(3):361-371. doi: 10.1002/path.6194. Epub 2023 Sep 21. J Pathol. 2023. PMID: 37735782 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Phosphodiesterase 4 in Gastrointestinal and Liver Diseases: From Isoform-Specific Mechanisms to Precision Therapeutics.Biomedicines. 2025 May 23;13(6):1285. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13061285. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40564004 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An Overview of PDE4 Inhibitors in Clinical Trials: 2010 to Early 2022.Molecules. 2022 Aug 4;27(15):4964. doi: 10.3390/molecules27154964. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35956914 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic perspectives on PDE4B inhibition in adipose tissue dysfunction and chronic liver injury.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2024 Jul;28(7):545-573. doi: 10.1080/14728222.2024.2369590. Epub 2024 Jun 19. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2024. PMID: 38878273 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Complexity and Multiplicity of the Specific cAMP Phosphodiesterase Family: PDE4, Open New Adapted Therapeutic Approaches.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 13;23(18):10616. doi: 10.3390/ijms231810616. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36142518 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

