Fluid Dynamics Experiments for Planetary Interiors
- PMID: 35535259
- PMCID: PMC9050801
- DOI: 10.1007/s10712-021-09681-1
Fluid Dynamics Experiments for Planetary Interiors
Abstract
Understanding fluid flows in planetary cores and subsurface oceans, as well as their signatures in available observational data (gravity, magnetism, rotation, etc.), is a tremendous interdisciplinary challenge. In particular, it requires understanding the fundamental fluid dynamics involving turbulence and rotation at typical scales well beyond our day-to-day experience. To do so, laboratory experiments are fully complementary to numerical simulations, especially in systematically exploring extreme flow regimes for long duration. In this review article, we present some illustrative examples where experimental approaches, complemented by theoretical and numerical studies, have been key for a better understanding of planetary interior flows driven by some type of mechanical forcing. We successively address the dynamics of flows driven by precession, by libration, by differential rotation, and by boundary topography.
Keywords: Instabilities; Planetary cores; Rotational fluid dynamics; Subsurface oceans; Turbulence; Waves.
© The Author(s) 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
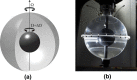
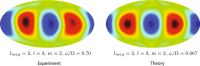
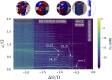

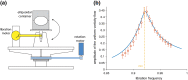
References
-
- Aldridge KD, Toomre A. Axisymmetric inertial oscillations of a fluid in a rotating spherical container. J Fluid Mech. 1969;37(2):307. doi: 10.1017/S0022112069000565. - DOI
-
- Aubert J, Gastine T, Fournier A. Spherical convective dynamos in the rapidly rotating asymptotic regime. J Fluid Mech. 2017;813:558. doi: 10.1017/jfm.2016.789. - DOI
-
- Balbus SA, Hawley JF. Instability, turbulence, and enhanced transport in accretion disks. Rev Mod Phys. 1998;70(1):1. doi: 10.1103/RevModPhys.70.1. - DOI
-
- Barik A, Triana SA, Hoff M, Wicht J. Triadic resonances in the wide-gap spherical Couette system. J Fluid Mech. 2018;843:211. doi: 10.1017/jfm.2018.138. - DOI
-
- Bell PI, Soward AM. The influence of surface topography on rotating convection. J Fluid Mech. 1996;313:147. doi: 10.1017/S0022112096002169. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
