Sex and chronic stress alter the distribution of glutamate receptors within rat hippocampal CA3 pyramidal cells following oxycodone conditioned place preference
- PMID: 35535260
- PMCID: PMC9076964
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ynstr.2022.100431
Sex and chronic stress alter the distribution of glutamate receptors within rat hippocampal CA3 pyramidal cells following oxycodone conditioned place preference
Abstract
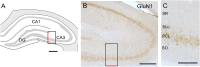
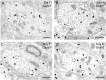
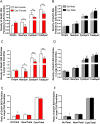
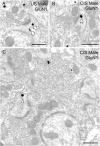
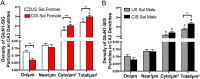
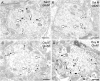
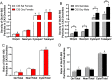
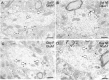
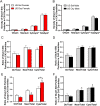
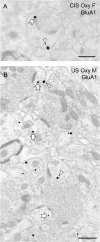
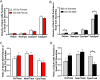
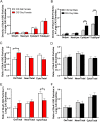
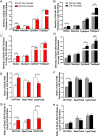
Glutamate receptors have a key role in the neurobiology of opioid addiction. Using electron microscopic immunocytochemical methods, this project elucidates how sex and chronic immobilization stress (CIS) impact the redistribution of GluN1 and GluA1 within rat hippocampal CA3 pyramidal cells following oxycodone (Oxy) conditioned place preference (CPP). Four groups of female and male Sprague-Dawley rats subjected to CPP were used: Saline- (Sal) and Oxy-injected (3 mg/kg, I.P.) naïve rats; and Sal- and Oxy-injected CIS rats. GluN1: In both naive and CIS rats, Sal-females compared to Sal-males had elevated cytoplasmic and total dendritic GluN1. Following Oxy CPP, near plasmalemmal, cytoplasmic, and total GluN1 decreased in CA3 dendrites of unstressed females suggesting reduced pools of GluN1 available for ligand binding. Following CIS, Oxy-males (which did not acquire CPP) had increased GluN1 in all compartments of dendrites and spines of CA3 neurons. GluA1: There were no differences in the distribution GluA1 in any cellular compartments of CA3 dendrites in naïve females and males following either Sal or Oxy CPP. CIS alone increased the percent of GluA1 in CA3 dendritic spines in males compared to females. CIS Oxy-males compared to CIS Sal-males had an increase in cytoplasmic and total dendritic GluA1. Thus, in CIS Oxy-males increased pools of GluN1 and GluA1 are available for ligand binding in CA3 neurons. Together with our prior experiments, these changes in GluN1 and GluA1 following CIS in males may contribute to an increased sensitivity of CA3 neurons to glutamate excitation and a reduced capacity to acquire Oxy CPP.
Keywords: ABC, avidin-biotin complex; AMPA receptors; BSA, bovine serum albumin; CIS, chronic immobilization stress; CPP, conditioned place preference; DAB, diaminobenzidine; DG, dentate gyrus; DOR, delta opioid receptor; Drug associative-learning; Electron microscopy; GABA, Gamma-amino butyric acid; GluA1, AMPA glutamate receptor subunit 1; GluN1, NMDA, glutamate receptor subunit 1; LTP, long-term potentiation; MOR, mu opioid receptor; NMDA receptors; NMDA, N-methyl-D-aspartate; NPY, neuropeptide Y; Oxy, oxycodone; PARV, parvalbumin; PB, phosphate buffer; PFA, paraformaldehyde; PM, plasma membrane; Pyramidal cells; ROI, region of interest; SLM, stratum lacunosum-moleculare; SLu, stratum lucidum; SO, stratum oriens; SOM, somatostatin; SR, stratum radiatum; Sal, saline; TS, tris-buffered saline; ir, immunoreactivity.
© 2022 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Chronic immobilization stress primes the hippocampal opioid system for oxycodone-associated learning in female but not male rats.Synapse. 2019 May;73(5):e22088. doi: 10.1002/syn.22088. Epub 2019 Jan 22. Synapse. 2019. PMID: 30632204 Free PMC article.
-
Sex and chronic stress alter delta opioid receptor distribution within rat hippocampal CA1 pyramidal cells following behavioral challenges.Neurobiol Stress. 2020 Jun 22;13:100236. doi: 10.1016/j.ynstr.2020.100236. eCollection 2020 Nov. Neurobiol Stress. 2020. PMID: 33344692 Free PMC article.
-
Sex and chronic stress differentially alter phosphorylated mu and delta opioid receptor levels in the rat hippocampus following oxycodone conditioned place preference.Neurosci Lett. 2019 Nov 20;713:134514. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2019.134514. Epub 2019 Sep 24. Neurosci Lett. 2019. PMID: 31560995 Free PMC article.
-
Oxycodone injections not paired with conditioned place preference have little effect on the hippocampal opioid system in female and male rats.Synapse. 2021 Jan;75(1):e22182. doi: 10.1002/syn.22182. Epub 2020 Jul 29. Synapse. 2021. PMID: 32654187
-
Sex differences in the rodent hippocampal opioid system following stress and oxycodone associated learning processes.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2022 Jan;212:173294. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2021.173294. Epub 2021 Nov 6. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2022. PMID: 34752798 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Special issue dedicated to Dr. Bruce S. McEwen.Neurobiol Stress. 2023 Jun 6;25:100552. doi: 10.1016/j.ynstr.2023.100552. eCollection 2023 Jul. Neurobiol Stress. 2023. PMID: 37547772 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Akashi K., Kakizaki T., Kamiya H., Fukaya M., Yamasaki M., Abe M., Natsume R., Watanabe M., Sakimura K. NMDA receptor GluN2B (GluR epsilon 2/NR2B) subunit is crucial for channel function, postsynaptic macromolecular organization, and actin cytoskeleton at hippocampal CA3 synapses. J. Neurosci. 2009;29:10869–10882. - PMC - PubMed
-
- American Addiction Centers . American Addiction Centers; 2020. How Hormones Affect Addiction.
-
- Ashirova E., Contoreggi N.H., Johnson M.A., Al-Khayat F.J., Calcano G.A., Rubin B.R., O'Cinneide E.M., Zhang Y., Zhou Y., Gregoire L., McEwen B.S., Kreek M.J., Milner T.A. Oxycodone injections not paired with conditioned place preference have little effect on the hippocampal opioid system in female and male rats. Synapse. 2021;75 - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

