Delayed Rupture of an Anterior Communicating Artery Pseudoaneurysm Caused by Distal Occlusion Thrombectomy Using a Stent Retriever: A Case Report and Mechanism of Injury
- PMID: 35535378
- PMCID: PMC9256472
- DOI: 10.5469/neuroint.2022.00101
Delayed Rupture of an Anterior Communicating Artery Pseudoaneurysm Caused by Distal Occlusion Thrombectomy Using a Stent Retriever: A Case Report and Mechanism of Injury
Abstract
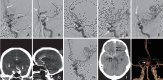
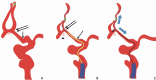
We report a case of delayed rupture of an anterior communicating artery (Acom) pseudoaneurysm following mechanical thrombectomy (MT) of a distal artery occlusion using a stent retriever. An elderly patient with right hemiparesis showed left proximal internal cerebral artery and middle cerebral artery occlusions. During MT, a fragmented thrombus moved to the anterior cerebral artery (ACA). A stent retriever was deployed to the occluded ACA, and the Acom and proximal ACA segment were significantly straightened. Additionally, we attempted a blind exchange mini-pinning (BEMP) technique, but a subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) occurred. Bleeding was almost entirely absorbed 9 days after the procedure, but the SAH recurred at 20 days, and computed tomography angiography revealed a new pseudoaneurysm formation in the Acom. We suggest that the proposed mechanism of pseudoaneurysm formation was likely due to the dislocation and avulsion of the Acom perforators when the ipsilateral ACA was pushed and pulled during MT.
Keywords: Acute ischemic stroke; Pseudoaneurysm; Subarachnoid hemorrhage; Thrombectomy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Imahori T, Okamura Y, Sakata J, Shose H, Yamanishi S, Kohmura E. Delayed rebleeding from pseudoaneurysm after mechanical thrombectomy using stent retriever due to small artery avulsion confirmed by open surgery. World Neurosurg. 2020;133:150–154. - PubMed
-
- Misaki K, Uchiyama N, Mohri M, Kamide T, Tsutsui T, Kanamori N, et al. Pseudoaneurysm formation caused by the withdrawal of a Trevo ProVue stent at a tortuous cerebral vessel: a case report. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 2016;158:2085–2088. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

