Detection of SARS-CoV-2 in different human biofluids using the loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay: A prospective diagnostic study in Fortaleza, Brazil
- PMID: 35535440
- PMCID: PMC9348339
- DOI: 10.1002/jmv.27842
Detection of SARS-CoV-2 in different human biofluids using the loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay: A prospective diagnostic study in Fortaleza, Brazil
Abstract
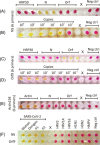
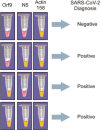
We adopted the reverse-transcriptase-loop-mediated isothermal amplification (RT-LAMP) to detect severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-Cov-2) in patient samples. Two primer sets for genes N and Orf1ab were designed to detect SARS-CoV-2, and one primer set was designed to detect the human gene Actin. We collected prospective 138 nasopharyngeal swabs, 70 oropharyngeal swabs, 69 salivae, and 68 mouth saline wash samples from patients suspected to have severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) caused by SARS-CoV-2 to test the RT-LAMP in comparison with the gold standard technique reverse-transcription quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR). The accuracy of diagnosis using both primers, N5 and Orf9, was evaluated. Sensitivity and specificity for diagnosis were 96% (95% confidence interval [CI]: 87-99) and 85% (95% CI: 76-91) in 138 samples, respectively. Accurate diagnosis results were obtained only in nasopharyngeal swabs processed via extraction kit. Accurate and rapid diagnosis could aid coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic management by identifying, isolating, and treating patients rapidly.
Keywords: RT-LAMP; coronavirus; molecular diagnosis.
© 2022 Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Yamazaki W, Taguchi M, Ishibashi M, et al. Development and evaluation of a loop‐mediated isothermal amplification assay for rapid and simple detection of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli. J Med Microbiol. 2008;57(Pt 4):444‐451. - PubMed
-
- Ito M, Watanabe M, Nakagawa N, Ihara T, Okuno Y. Rapid detection and typing of influenza A and B by loop‐mediated isothermal amplification: comparison with immunochromatography and virus isolation. J Virol Methods. 2006;135(2):272‐275. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

