Who prescribes quetiapine in Denmark?
- PMID: 35535441
- PMCID: PMC9545446
- DOI: 10.1111/bcp.15388
Who prescribes quetiapine in Denmark?
Abstract
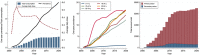
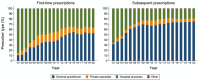
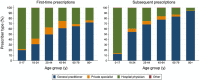
The second-generation antipsychotic quetiapine is commonly used off-label for its anxiolytic and hypnotic properties. However, quetiapine is associated with problematic side-effects. We used Danish Medicinal Product Statistics and a 20% random sample of the Danish population's prescription fills (2001-2020) to describe the utilization of quetiapine and proportion of various prescriber types (general practitioner [GP], specialist in private practice, hospital physician and other prescribers) both in connection to first-time and subsequent prescriptions. In 2020, 92% of all quetiapine was dispensed outside hospitals and the average daily dispensed quantity of quetiapine per user corresponded to 100 mg/user/d. A GP issued 53% of first-time prescriptions and 75% of subsequent prescriptions for quetiapine in 2020. The proportion of quetiapine prescriptions issued by GPs varied by age group-from 14% among 0-17-year-olds to 93% among the ≥80-year-olds. Future initiatives on the rational use of quetiapine and related drugs, especially among adults, should target GPs.
Keywords: antipsychotics; off-label; prescriber; quetiapine.
© 2022 The Authors. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of British Pharmacological Society.
Conflict of interest statement
Mikkel Højlund reports personal honoraria for consultancy/lecturing from the Lundbeck Foundation and Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. unrelated to this work. Lotte Rasmussen reports participation in research projects funded by Novo Nordisk with no relation to the work reported in this paper. Anton Pottegård reports participation in research projects funded by Alcon, Almirall, Astellas, AstraZeneca, Boehringer‐Ingelheim, Novo Nordisk, Servier and LEO Pharma, all regulator‐mandated phase IV‐studies, all with funds paid to the institution where he was employed (no personal fees) and with no relation to the work reported in this paper. The remaining authors reports no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- European Medicines Agency . Summary of product characteristics: Seroquel, Seroquel XR and associated names (quetiapine). Accessed January 6, 2022. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/referral/seroquel-seroquel-xr-ass...
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

