Putative therapeutic impacts of cardiac CTRP9 in ischaemia/reperfusion injury
- PMID: 35535510
- PMCID: PMC9170823
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.17355
Putative therapeutic impacts of cardiac CTRP9 in ischaemia/reperfusion injury
Abstract
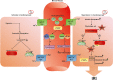
Recently, cytokines belonging to C1q/tumour necrosis factor-related proteins (CTRPs) superfamily have attracted increasing attention due to multiple metabolic functions and desirable anti-inflammatory effects. These various molecular effectors exhibit key roles upon the onset of cardiovascular diseases, making them novel adipo/cardiokines. This review article aimed to highlight recent findings correlated with therapeutic effects and additional mechanisms specific to the CTRP9, particularly in cardiac ischaemia/reperfusion injury (IRI). Besides, the network of the CTPR9 signalling pathway and its possible relationship with IRI were discussed. Together, the discovery of all involved underlying mechanisms could shed light to alleviate the pathological sequelae after the occurrence of IRI.
Keywords: CTRP9; ischaemia/reperfusion injury; signalling pathways; therapeutic target.
© 2022 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Inhibition of CTRP9, a novel and cardiac-abundantly expressed cell survival molecule, by TNFα-initiated oxidative signaling contributes to exacerbated cardiac injury in diabetic mice.Basic Res Cardiol. 2013 Jan;108(1):315. doi: 10.1007/s00395-012-0315-z. Epub 2012 Dec 5. Basic Res Cardiol. 2013. PMID: 23212557 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiac-derived CTRP9 protects against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury via calreticulin-dependent inhibition of apoptosis.Cell Death Dis. 2018 Jun 20;9(7):723. doi: 10.1038/s41419-018-0726-3. Cell Death Dis. 2018. PMID: 29925877 Free PMC article.
-
Detrimental effects of prolonged warm renal ischaemia-reperfusion injury are abrogated by supplemental hydrogen sulphide: an analysis using real-time intravital microscopy and polymerase chain reaction.BJU Int. 2012 Dec;110(11 Pt C):E1218-27. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410X.2012.11555.x. Epub 2012 Oct 9. BJU Int. 2012. PMID: 23046222
-
CTRP9: An emerging potential anti-aging molecule in brain.Cell Signal. 2020 Sep;73:109694. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2020.109694. Epub 2020 Jun 12. Cell Signal. 2020. PMID: 32540339 Review.
-
Molecular mechanisms of liver ischemia reperfusion injury: insights from transgenic knockout models.World J Gastroenterol. 2013 Mar 21;19(11):1683-98. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i11.1683. World J Gastroenterol. 2013. PMID: 23555157 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
CTRP9 attenuates peripheral nerve injury-induced mechanical allodynia and thermal hyperalgesia through regulating spinal microglial polarization and neuroinflammation mediated by AdipoR1 in male mice.Cell Biol Toxicol. 2024 Oct 26;40(1):91. doi: 10.1007/s10565-024-09933-x. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 39460844 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bainey KR, Armstrong PW. Clinical perspectives on reperfusion injury in acute myocardial infarction. Am Heart J. 2014;167(5):637‐645. - PubMed
-
- Ong S‐B, Katwadi K, Kwek X‐Y, et al. Non‐coding RNAs as therapeutic targets for preventing myocardial ischemia‐reperfusion injury. Exp Opin Ther Targets. 2018;22(3):247‐261. - PubMed
-
- Miller MA, Zachary JF. Mechanisms and morphology of cellular injury, adaptation, and death. Pathol Basis Vet Dis. 2017:2‐43.e19.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

