The α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor agonist PNU-282987 ameliorates sepsis-induced acute kidney injury through CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells in rats
- PMID: 35535600
- PMCID: PMC9589307
- DOI: 10.17305/bjbms.2022.7111
The α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor agonist PNU-282987 ameliorates sepsis-induced acute kidney injury through CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells in rats
Abstract
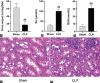
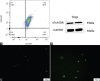
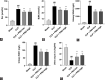
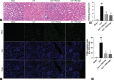
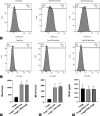
The ameliorative effects of α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (α7nAChR) agonists have been demonstrated in acute kidney injury (AKI) caused by multiple stimulations. However, the ameliorative effect of α7nAChR on sepsis-induced acute kidney injury (SAKI) in the cecal ligation and puncture (CLP) model is unclear. Previous studies have demonstrated that α7nAChR is highly expressed on the surface of CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells (Tregs). However, the role of Tregs in SAKI is unclear. We hypothesized that Tregs might play a role in the ameliorative effect of α7nAChR on SAKI. Hence, in this study, we determined the effects of PNU-282987 (a selective α7nAchR agonist) on SAKI and evaluated whether PNU-282987 would attenuate SAKI via regulating Tregs. Our study showed that immediate administration of PNU-282987 after CLP surgery in rats improved renal function, reduced levels of systemic inflammatory factors (tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin-6 (IL-6), etc.), inflammatory cell infiltration and tubular apoptosis in renal tissues, and increased forkhead/winged helix transcription factor p3 (Foxp3) and cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4 (CTLA-4) expression indicating activated Tregs. Moreover, in in vitro experiments, isolated Tregs co-cultured with PNU-282987 also displayed enhanced expression of CTLA-4 and Foxp3. Furthermore, Tregs were co-cultured with PNU-282987 for 24 hours and then reinfused into rats through the tail vein immediately after CLP surgery, and a significant renal protective effect was observed 24 hours postoperatively. These results demonstrate that PNU-282987 exerts its renal protective effects on SAKI through activation of Tregs.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Sunggoro AJ, Arifin A, Marwanta S, Atmodjo SM, Maryono S. 536P Characteristics and outcome of cancer patients with sepsis requiring admission to the intensive care unit. Ann Oncol. 2016;27:ix174. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0923-7534(21)00694-3.
-
- See EJ, Jayasinghe K, Glassford N, Bailey M, Johnson DW, Polkinghorne KR, et al. Long-term risk of adverse outcomes after acute kidney injury:A systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies using consensus definitions of exposure. Kidney Int. 2019;95(1):160–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.kint.2018.08.036. - PubMed
-
- Bellomo R, Kellum JA, Ronco C, Wald R, Martensson J, Maiden M, et al. Acute kidney injury in sepsis. Intensive Care Med. 2017;43(6):816–28. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-017-4755-7. - PubMed
-
- van der Slikke EC, Star BS, van Meurs M, Henning RH, Moser J, Bouma HR. Sepsis is associated with mitochondrial DNA damage and a reduced mitochondrial mass in the kidney of patients with sepsis-AKI. Crit Care. 2021;25(1):36. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13054-020-03424-1. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gómez H, Kellum JA. Sepsis-induced acute kidney injury. Curr Opin Crit Care. 2016;22:524–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-323-44942-7.00090-x. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

