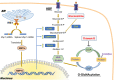
Targeting O-GlcNAcylation in ischemic stroke
- PMID: 35535885
- PMCID: PMC9120690
- DOI: 10.4103/1673-5374.335806
Targeting O-GlcNAcylation in ischemic stroke
Figures
References
-
- Hwang SY, Shin JH, Hwang JS, Kim SY, Shin JA, Oh ES, Oh S, Kim JB, Lee JK, Han IO. Glucosamine exerts a neuroprotective effect via suppression of inflammation in rat brain ischemia/reperfusion injury. Glia. 2010;58:1881–1892. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

