A three-dimensional matrix system containing melatonin and neural stem cells repairs damage from traumatic brain injury in rats
- PMID: 35535904
- PMCID: PMC9120671
- DOI: 10.4103/1673-5374.339001
A three-dimensional matrix system containing melatonin and neural stem cells repairs damage from traumatic brain injury in rats
Abstract
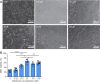
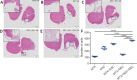
Brain lesions can cause neural stem cells to activate, proliferate, differentiate, and migrate to the injured area. However, after traumatic brain injury, brain tissue defects and microenvironment changes greatly affect the survival and growth of neural stem cells; the resulting reduction in the number of neural stem cells impedes effective repair of the injured area. Melatonin can promote the survival, proliferation, and differentiation of neural stem cells under adverse conditions such as oxidative stress or hypoxia that can occur after traumatic brain injury. Therefore, we investigated the therapeutic effects of melatonin combined with neural stem cells on traumatic brain injury in rats. First, in vitro studies confirmed that melatonin promoted the survival of neural stem cells deprived of oxygen and glucose. Then, we established a three-dimensional Matrigel-based transplantation system containing melatonin and neural stem cells and then used it to treat traumatic brain injury in rats. We found that treatment with the Matrigel system containing melatonin and neural stem cells decreased brain lesion volume, increased the number of surviving neurons, and improved recovery of neurological function compared with treatment with Matrigel alone, neural stem cells alone, Matrigel and neural stem cells combined, and Matrigel and melatonin combined. Our findings suggest that the three-dimensional Matrigel-based transplantation system containing melatonin and neural stem cells is a potential treatment for traumatic brain injury.
Keywords: Matrigel; cell therapy; magnetic resonance imaging; melatonin; neural stem cells; neurological function recovery; three-dimensional transplantation; traumatic brain injury.
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures






Similar articles
-
Benefits of the Neurogenic Potential of Melatonin for Treating Neurological and Neuropsychiatric Disorders.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 2;24(5):4803. doi: 10.3390/ijms24054803. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36902233 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The effect of Matrigel as scaffold material for neural stem cell transplantation for treating spinal cord injury.Sci Rep. 2020 Feb 13;10(1):2576. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-59148-3. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32054865 Free PMC article.
-
Transplantation of RADA16-BDNF peptide scaffold with human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells forced with CXCR4 and activated astrocytes for repair of traumatic brain injury.Acta Biomater. 2016 Nov;45:247-261. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2016.09.001. Epub 2016 Sep 2. Acta Biomater. 2016. PMID: 27592818
-
Transplantation of human meningioma stem cells loaded on a self-assembling peptide nanoscaffold containing IKVAV improves traumatic brain injury in rats.Acta Biomater. 2019 Jul 1;92:132-144. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2019.05.010. Epub 2019 May 7. Acta Biomater. 2019. PMID: 31075516
-
Therapeutic Application of Stem Cells in the Repair of Traumatic Brain Injury.Stem Cells Cloning. 2022 Jul 13;15:53-61. doi: 10.2147/SCCAA.S369577. eCollection 2022. Stem Cells Cloning. 2022. PMID: 35859889 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Multiple Functions of Melatonin: Applications in the Military Setting.Biomedicines. 2022 Dec 21;11(1):5. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11010005. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36672513 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tetrahydrofolate Attenuates Cognitive Impairment after Hemorrhagic Stroke by Promoting Hippocampal Neurogenesis via PTEN Signaling.eNeuro. 2024 Jun 3;11(6):ENEURO.0021-24.2024. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0021-24.2024. Print 2024 Jun. eNeuro. 2024. PMID: 38729764 Free PMC article.
-
Benefits of the Neurogenic Potential of Melatonin for Treating Neurological and Neuropsychiatric Disorders.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 2;24(5):4803. doi: 10.3390/ijms24054803. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36902233 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic pathways in cerebral palsy: a review of the implications for precision diagnosis and understanding disease mechanisms.Neural Regen Res. 2024 Jul 1;19(7):1499-1508. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.385855. Epub 2023 Sep 22. Neural Regen Res. 2024. PMID: 38051892 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

