In vivo neuronal and astrocytic activation in somatosensory cortex by acupuncture stimuli
- PMID: 35535906
- PMCID: PMC9120680
- DOI: 10.4103/1673-5374.339003
In vivo neuronal and astrocytic activation in somatosensory cortex by acupuncture stimuli
Abstract
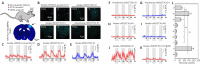
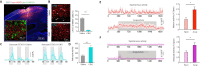
Acupuncture is a medical treatment that has been widely practiced in China for over 3000 years, yet the neural mechanisms of acupuncture are not fully understood. We hypothesized that neurons and astrocytes act independently and synergistically under acupuncture stimulation. To investigate this, we used two-photon in vivo calcium recording to observe the effects of acupuncture stimulation at ST36 (Zusanli) in mice. Acupuncture stimulation in peripheral acupoints potentiated calcium signals of pyramidal neurons and astrocytes in the somatosensory cortex and resulted in late-onset calcium transients in astrocytes. Chemogenetic inhibition of neurons augmented the astrocytic activity. These findings suggest that acupuncture activates neuronal and astrocytic activity in the somatosensory cortex and provide evidence for the involvement of both neurons and astrocytes in acupuncture treatment.
Keywords: N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor; acupuncture; astrocyte; chemogenetic; imaging; neuron; somatosensory cortex; transient receptor potential A1; two-photon in vivo.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
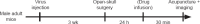

References
-
- Aronoff R, Matyas F, Mateo C, Ciron C, Schneider B, Petersen CC. Long-range connectivity of mouse primary somatosensory barrel cortex. Eur J Neurosci. 2010;31:2221–2233. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

