Obstructive sleep apnea aggravates neuroinflammation and pyroptosis in early brain injury following subarachnoid hemorrhage via ASC/HIF-1α pathway
- PMID: 35535908
- PMCID: PMC9120669
- DOI: 10.4103/1673-5374.339000
Obstructive sleep apnea aggravates neuroinflammation and pyroptosis in early brain injury following subarachnoid hemorrhage via ASC/HIF-1α pathway
Abstract
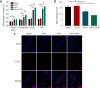
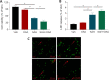
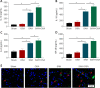
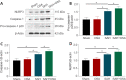
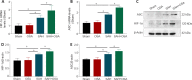
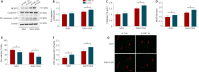
Obstructive sleep apnea can worsen the prognosis of subarachnoid hemorrhage. However, the underlying mechanism remains unclear. In this study, we established a mouse model of subarachnoid hemorrhage using the endovascular perforation method and exposed the mice to intermittent hypoxia for 8 hours daily for 2 consecutive days to simulate sleep apnea. We found that sleep apnea aggravated brain edema, increased hippocampal neuron apoptosis, and worsened neurological function in this mouse model of subarachnoid hemorrhage. Then, we established an in vitro HT-22 cell model of hemin-induced subarachnoid hemorrhage/intermittent hypoxia and found that the cells died, and lactate dehydrogenase release increased, after 48 hours. We further investigated the underlying mechanism and found that sleep apnea increased the expression of hippocampal neuroinflammatory factors interleukin-1β, interleukin-18, interleukin-6, nuclear factor κB, pyroptosis-related protein caspase-1, pro-caspase-1, and NLRP3, promoted the proliferation of astrocytes, and increased the expression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1α and apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a CARD, which are the key proteins in the hypoxia-inducible factor 1α/apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a CARD signaling pathway. We also found that knockdown of hypoxia-inducible factor 1α expression in vitro greatly reduced the damage to HY22 cells. These findings suggest that sleep apnea aggravates early brain injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage by aggravating neuroinflammation and pyroptosis, at least in part through the hypoxia-inducible factor 1α/apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a CARD signaling pathway.
Keywords: apoptosis associated speck like protein containing a CARD; early brain injury; hypoxia-inducible factor 1α; neuroinflammation; nucleotide-binding domain and leucine-rich repeat protein 3; obstructive sleep apnea; pyroptosis; subarachnoid hemorrhage.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
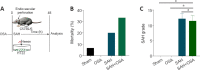
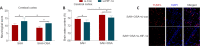
Similar articles
-
Hydrogen-Rich Saline Attenuated Subarachnoid Hemorrhage-Induced Early Brain Injury in Rats by Suppressing Inflammatory Response: Possible Involvement of NF-κB Pathway and NLRP3 Inflammasome.Mol Neurobiol. 2016 Jul;53(5):3462-3476. doi: 10.1007/s12035-015-9242-y. Epub 2015 Jun 20. Mol Neurobiol. 2016. PMID: 26091790
-
Inhibition of the glycogen synthase kinase 3β-hypoxia-inducible factor 1α pathway alleviates NLRP3-mediated pyroptosis induced by high glucose in renal tubular epithelial cells.Exp Physiol. 2022 Dec;107(12):1493-1506. doi: 10.1113/EP090685. Epub 2022 Sep 26. Exp Physiol. 2022. PMID: 36056793
-
Intermittent hypoxia mimicking obstructive sleep apnea aggravates early brain injury following ICH via neuroinflammation and apoptosis.Mol Med Rep. 2021 Nov;24(5):824. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2021.12464. Epub 2021 Sep 24. Mol Med Rep. 2021. PMID: 34558649 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia and Porphyromonas gingivalis-lipopolysaccharide synergistically induce NLRP3 inflammasome activation in human gingival fibroblasts.Int Immunopharmacol. 2021 May;94:107456. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2021.107456. Epub 2021 Feb 12. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33588175
-
Hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF): The link between obesity and COVID-19.Obes Med. 2021 Mar;22:100317. doi: 10.1016/j.obmed.2020.100317. Epub 2020 Dec 30. Obes Med. 2021. PMID: 33521378 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cytosolic Escape of Mitochondrial DNA Triggers cGAS-STING Pathway-Dependent Neuronal PANoptosis in Response to Intermittent Hypoxia.Neurochem Res. 2024 Aug;49(8):2228-2248. doi: 10.1007/s11064-024-04151-7. Epub 2024 Jun 4. Neurochem Res. 2024. PMID: 38833090
-
Neuronal nitric oxide synthase/reactive oxygen species pathway is involved in apoptosis and pyroptosis in epilepsy.Neural Regen Res. 2023 Jun;18(6):1277-1285. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.357906. Neural Regen Res. 2023. PMID: 36453412 Free PMC article.
-
Oxygen desaturation index, lowest arterial oxygen saturation and time spent below 90% oxygen saturation as diagnostic markers for obstructive sleep apnea.Am J Transl Res. 2023 May 15;15(5):3597-3606. eCollection 2023. Am J Transl Res. 2023. PMID: 37303658 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic Intermittent Hypoxia-Induced Neural Injury: Pathophysiology, Neurodegenerative Implications, and Therapeutic Insights.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2025 Apr;31(4):e70384. doi: 10.1111/cns.70384. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2025. PMID: 40260643 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mitochondrial dysfunction and quality control lie at the heart of subarachnoid hemorrhage.Neural Regen Res. 2024 Apr;19(4):825-832. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.381493. Neural Regen Res. 2024. PMID: 37843218 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alim I, Caulfield JT, Chen Y, Swarup V, Geschwind DH, Ivanova E, Seravalli J, Ai Y, Sansing LH, Ste Marie EJ, Hondal RJ, Mukherjee S, Cave JW, Sagdullaev BT, Karuppagounder SS, Ratan RR. Selenium drives a transcriptional adaptive program to block ferroptosis and treat stroke. Cell. 2019;177:1262–1279. e25. - PubMed
-
- Bir SC, Nanda A, Cuellar H, Sun H, Guthikonda B, Liendo C, Minagar A, Chernyshev OY. Coexistence of obstructive sleep apnea worsens the overall outcome of intracranial aneurysm: a pioneer study. J Neurosurg. 2018;128:735–746. - PubMed
-
- Chen JH, Yang LK, Chen L, Wang YH, Wu Y, Jiang BJ, Zhu J, Li PP. Atorvastatin ameliorates early brain injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage via inhibition of AQP4 expression in rabbits. Int J Mol Med. 2016a;37:1059–1066. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

