Combining radiation with PI3K isoform-selective inhibitor administration increases radiosensitivity and suppresses tumor growth in non-small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 35536306
- PMCID: PMC9303607
- DOI: 10.1093/jrr/rrac018
Combining radiation with PI3K isoform-selective inhibitor administration increases radiosensitivity and suppresses tumor growth in non-small cell lung cancer
Abstract
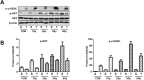
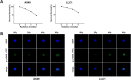
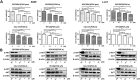
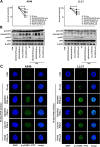
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is a malignant lung tumor with a dismal prognosis. The activation of the phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)/AKT signaling pathway is common in many tumor types including NSCLC, which results in radioresistance and changes in the tumor microenvironment. Although pan-PI3K inhibitors have been tested in clinical trials to overcome radioresistance, concerns regarding their excessive side effects led to the consideration of selective inhibition of PI3K isoforms. In this study, we assessed whether combining radiation with the administration of the PI3K isoform-selective inhibitors reduces radioresistance and tumor growth in NSCLC. Inhibition of the PI3K/AKT pathway enhanced radiosensitivity substantially, and PI3K-α inhibitor showed superior radiosensitizing effect similar to PI3K pan-inhibitor, both in vitro and in vivo. Additionally, a significant increase in DNA double-strand breaks (DSB) and a decrease in migration ability were observed. Our study revealed that combining radiation and the PI3K-α isoform improved radiosensitivity that resulted in a significant delay in tumor growth and improved survival rate.
Keywords: PI3K isoform; non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC); radiation; radioresistance; radiosensitivity.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of The Japanese Radiation Research Society and Japanese Society for Radiation Oncology.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Selective Inhibition of PI3K Isoforms in Brain Tumors Suppresses Tumor Growth by Increasing Radiosensitivity.Yonsei Med J. 2023 Feb;64(2):139-147. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2022.0414. Yonsei Med J. 2023. PMID: 36719022 Free PMC article.
-
SIRT6 through PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway to enhance radiosensitivity of non-Small cell lung cancer and inhibit tumor progression.IUBMB Life. 2021 Sep;73(9):1092-1102. doi: 10.1002/iub.2511. Epub 2021 Jun 4. IUBMB Life. 2021. PMID: 34033225
-
Dual targeting of PI3K and MEK enhances the radiation response of K-RAS mutated non-small cell lung cancer.Oncotarget. 2016 Jul 12;7(28):43746-43761. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.9670. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27248324 Free PMC article.
-
The PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway inhibitors enhance radiosensitivity in cancer cell lines.Mol Biol Rep. 2021 Aug;48(8):1-14. doi: 10.1007/s11033-021-06607-3. Epub 2021 Aug 6. Mol Biol Rep. 2021. PMID: 34357550 Review.
-
The PI3-K/AKT-pathway and radiation resistance mechanisms in non-small cell lung cancer.J Thorac Oncol. 2009 Jun;4(6):761-7. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0b013e3181a1084f. J Thorac Oncol. 2009. PMID: 19404218 Review.
Cited by
-
Triple‑negative breast cancer cells that survive ionizing radiation exhibit an Axl‑dependent aggressive radioresistant phenotype.Exp Ther Med. 2023 Aug 3;26(3):448. doi: 10.3892/etm.2023.12147. eCollection 2023 Sep. Exp Ther Med. 2023. PMID: 37614420 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted Therapy with PI3K, PARP, and WEE1 Inhibitors and Radiotherapy in HPV Positive and Negative Tonsillar Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cell Lines Reveals Synergy while Effects with APR-246 Are Limited.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Dec 23;15(1):93. doi: 10.3390/cancers15010093. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36612094 Free PMC article.
-
Selective Inhibition of PI3K Isoforms in Brain Tumors Suppresses Tumor Growth by Increasing Radiosensitivity.Yonsei Med J. 2023 Feb;64(2):139-147. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2022.0414. Yonsei Med J. 2023. PMID: 36719022 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting ataxia-telangiectasia mutated and cystine/glutamate antiporter enhances radiotherapy efficacy and tumor suppression in glioblastoma.J Neurooncol. 2025 Oct;175(1):267-277. doi: 10.1007/s11060-025-05128-4. Epub 2025 Jul 17. J Neurooncol. 2025. PMID: 40676327
-
WDR72 Enhances the Stemness of Lung Cancer Cells by Activating the AKT/HIF-1α Signaling Pathway.J Oncol. 2022 Nov 7;2022:5059588. doi: 10.1155/2022/5059588. eCollection 2022. J Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36385964 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin 2016;66:7–30. - PubMed
-
- Torre LA, Siegel RL, Ward EM et al. Global cancer incidence and mortality rates and trends--an update. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev 2016;25:16–27. - PubMed
-
- Kuwahara Y, Roudkenar MH, Urushihara Y et al. Clinically relevant radioresistant cell line: a simple model to understand cancer radioresistance. Med Mol Morphol 2017;50:195–204. - PubMed
-
- Chen Y, Wang BC, Xiao Y. PI3K: a potential therapeutic target for cancer. J Cell Physiol 2012;227:2818–21. - PubMed
-
- Toulany M, Lee KJ, Fattah KR et al. Akt promotes post-irradiation survival of human tumor cells through initiation, progression, and termination of DNA-PKcs-dependent DNA double-strand break repair. Mol Cancer Res 2012;10:945–57. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

