VMP1 and TMEM41B are essential for DMV formation during β-coronavirus infection
- PMID: 35536318
- PMCID: PMC9097365
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.202112081
VMP1 and TMEM41B are essential for DMV formation during β-coronavirus infection
Abstract
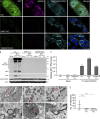
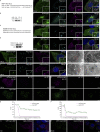
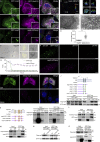
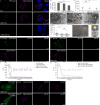
β-coronaviruses reshape host cell endomembranes to form double-membrane vesicles (DMVs) for genome replication and transcription. Ectopically expressed viral nonstructural proteins nsp3 and nsp4 interact to zipper and bend the ER for DMV biogenesis. Genome-wide screens revealed the autophagy proteins VMP1 and TMEM41B as important host factors for SARS-CoV-2 infection. Here, we demonstrated that DMV biogenesis, induced by virus infection or expression of nsp3/4, is impaired in the VMP1 KO or TMEM41B KO cells. In VMP1 KO cells, the nsp3/4 complex forms normally, but the zippered ER fails to close into DMVs. In TMEM41B KO cells, the nsp3-nsp4 interaction is reduced and DMV formation is suppressed. Thus, VMP1 and TMEM41B function at different steps during DMV formation. VMP1 was shown to regulate cross-membrane phosphatidylserine (PS) distribution. Inhibiting PS synthesis partially rescues the DMV defects in VMP1 KO cells, suggesting that PS participates in DMV formation. We provide molecular insights into the collaboration of host factors with viral proteins to remodel host organelles.
© 2022 Ji et al.
Figures


References
-
- Cortese, M., Santarella-Mellwig R., Schorb M., Boermel M., Mocaer K., Beckwith M.S., Templin R.M., Gross V., Pape C., Tischer C., et al. . 2020. Integrative imaging reveals SARS-CoV-2-induced reshaping of subcellular morphologies. Cell Host Microbe. 28:853–866.e5. 10.1016/j.chom.2020.11.003 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

