Management of Hepatic Encephalopathy Associated with Advanced Liver Disease
- PMID: 35536537
- PMCID: PMC9205788
- DOI: 10.1007/s40261-022-01146-6
Management of Hepatic Encephalopathy Associated with Advanced Liver Disease
Abstract
Hepatic encephalopathy (HE) is a very prevalent condition in patients with advanced liver disease and has a high recurrence rate. The pathophysiology has a multifactorial origin where hyperammonaemia and inflammation become particularly relevant. There are no HE-specific diagnostic tests, and diagnosis is usually made by taking into account the presence of suggestive and compatible clinical symptoms, the existence of a predisposing liver condition and ruling out other causes with similar clinical manifestations. Once the diagnosis of HE is established, it is essential to carry out an adequate classification based on the underlying liver disease, the intensity of clinical manifestations, the temporal course of the disease and the presence or absence of precipitating factors. Treatment should be aimed at decreasing the duration, intensity and consequences of episodes, preventing recurrence and limiting the impact of the disease in patients and their relatives.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there were no conflicts of interest.
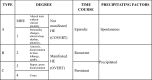
Figures

References
-
- Nolte W, Wiltfang J, Schindler C, et al. Portosystemic hepatic encephalopathy after transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt in patients with cirrhosis: clinical, laboratory, psychometric, and electroencephalographic investigations. Hepatology. 1998;28(5):1215–1225. doi: 10.1002/hep.510280508. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sharma BC, Sharma P, Agrawal A, Sarin SK. Secondary prophylaxis of hepatic encephalopathy: an open-label randomised controlled trial of lactulose versus placebo. Gastroenterology. 2009;137(885–91):891.e1. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

