The multifaceted functions of cGAS
- PMID: 35536585
- PMCID: PMC9475664
- DOI: 10.1093/jmcb/mjac031
The multifaceted functions of cGAS
Abstract
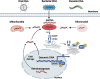
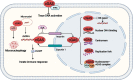
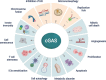
Pattern recognition receptors are critical for the sensing of pathogen-associated molecular patterns or danger-associated molecular patterns and subsequent mounting of innate immunity and shaping of adaptive immunity. The identification of 2'3'-cyclic guanosine monophosphate-adenosine monophosphate (cGAMP) synthase (cGAS) as a major cytosolic DNA receptor is a milestone in the field of DNA sensing. The engagement of cGAS by double-stranded DNA from different origins, including invading pathogens, damaged mitochondria, ruptured micronuclei, and genomic DNA results in the generation of cGAMP and activation of stimulator of interferon genes, which thereby activates innate immunity mainly characterized by the activation of type I interferon response. In recent years, great progress has been made in understanding the subcellular localization and novel functions of cGAS. In this review, we particularly focus on summarizing the multifaceted roles of cGAS in regulating senescence, autophagy, cell stemness, apoptosis, angiogenesis, cell proliferation, antitumor effect, DNA replication, DNA damage repair, micronucleophagy, as well as cell metabolism.
Keywords: DNA sensing; cyclic GMP–AMP synthase (cGAS); innate immunity; micronucleophagy; stimulator of interferon genes (STING).
© The Author(s) (2022). Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Journal of Molecular Cell Biology, CEMCS, CAS.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cyclic Guanosine Monophosphate-Adenosine Monophosphate Synthase (cGAS), a Multifaceted Platform of Intracellular DNA Sensing.Front Immunol. 2021 Feb 23;12:637399. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.637399. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33708225 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent progress on the activation of the cGAS-STING pathway and its regulation by biomolecular condensation.J Mol Cell Biol. 2022 Nov 29;14(6):mjac042. doi: 10.1093/jmcb/mjac042. J Mol Cell Biol. 2022. PMID: 35803579 Free PMC article.
-
Structures and Mechanisms in the cGAS-STING Innate Immunity Pathway.Immunity. 2020 Jul 14;53(1):43-53. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2020.05.013. Immunity. 2020. PMID: 32668227 Review.
-
Molecular mechanisms and cellular functions of cGAS-STING signalling.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2020 Sep;21(9):501-521. doi: 10.1038/s41580-020-0244-x. Epub 2020 May 18. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2020. PMID: 32424334 Review.
-
cGAS and cancer therapy: a double-edged sword.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2022 Sep;43(9):2202-2211. doi: 10.1038/s41401-021-00839-6. Epub 2022 Jan 18. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2022. PMID: 35042992 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The role of the cGAS-STING signaling pathway in viral infections, inflammatory and autoimmune diseases.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2024 Oct;45(10):1997-2010. doi: 10.1038/s41401-023-01185-5. Epub 2024 Jun 1. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2024. PMID: 38822084 Review.
-
The multi-functional roles of the cGAS-STING signaling pathway in health and diseases.J Mol Cell Biol. 2023 Feb 7;14(9):mjac057. doi: 10.1093/jmcb/mjac057. J Mol Cell Biol. 2023. PMID: 36748642 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Cyclic GMP-AMP Synthase in Cancer Prevention.J Cancer Prev. 2023 Dec 30;28(4):143-196. doi: 10.15430/JCP.2023.28.4.143. J Cancer Prev. 2023. PMID: 38205362 Free PMC article. Review.
-
cGAS: action in the nucleus.Front Immunol. 2024 Mar 7;15:1380517. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1380517. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38515746 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The STING in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Diseases: Potential Therapeutic Targets in Inflammation-Carcinogenesis Pathway.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Oct 9;15(10):1241. doi: 10.3390/ph15101241. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36297353 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ablasser A., Chen Z.J. (2019). cGAS in action: expanding roles in immunity and inflammation. Science 363, eaat8657. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

