Effective Storage of Electrons in Water by the Formation of Highly Reduced Polyoxometalate Clusters
- PMID: 35536652
- PMCID: PMC9171825
- DOI: 10.1021/jacs.1c10584
Effective Storage of Electrons in Water by the Formation of Highly Reduced Polyoxometalate Clusters
Abstract
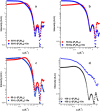
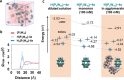
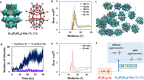
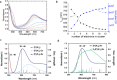
Aqueous solutions of polyoxometalates (POMs) have been shown to have potential as high-capacity energy storage materials due to their potential for multi-electron redox processes, yet the mechanism of reduction and practical limits are currently unknown. Herein, we explore the mechanism of multi-electron redox processes that allow the highly reduced POM clusters of the form {MO3}y to absorb y electrons in aqueous solution, focusing mechanistically on the Wells-Dawson structure X6[P2W18O62], which comprises 18 metal centers and can uptake up to 18 electrons reversibly (y = 18) per cluster in aqueous solution when the countercations are lithium. This unconventional redox activity is rationalized by density functional theory, molecular dynamics simulations, UV-vis, electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy, and small-angle X-ray scattering spectra. These data point to a new phenomenon showing that cluster protonation and aggregation allow the formation of highly electron-rich meta-stable systems in aqueous solution, which produce H2 when the solution is diluted. Finally, we show that this understanding is transferrable to other salts of [P5W30O110]15- and [P8W48O184]40- anions, which can be charged to 23 and 27 electrons per cluster, respectively.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures



References
-
- Sanchez C.; Livage J.; Launay J. P.; Fournier M. Electron Delocalization in Mixed-Valence Tungsten Polyanions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1983, 105, 6817–6823. 10.1021/ja00361a012. - DOI
-
- Liu J.; Cheng L.; Liu B.; Dong S. Covalent Modification of a Glassy Carbon Surface by 4-Aminobenzoic Acid and Its Application in Fabrication of a Polyoxometalates-Consisting Monolayer and Multilayer Films. Langmuir 2000, 16, 7471–7476. 10.1021/la9913506. - DOI
-
- Liu J.; Chen Z.; Chen S.; Zhang B.; Wang J.; Wang H.; Tian B.; Chen M.; Fan X.; Huang Y.; Sum T. C.; Lin J.; Shen Z. X. electron/Ion Sponge”-Like V-Based Polyoxometalate: Toward High-Performance Cathode for Rechargeable Sodium Ion Batteries. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 6911–6920. 10.1021/acsnano.7b02062. - DOI - PubMed

