Effective interventions to ensure MCH (Maternal and Child Health) services during pandemic related health emergencies (Zika, Ebola, and COVID-19): A systematic review
- PMID: 35536838
- PMCID: PMC9089853
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0268106
Effective interventions to ensure MCH (Maternal and Child Health) services during pandemic related health emergencies (Zika, Ebola, and COVID-19): A systematic review
Abstract
Introduction: Ensuring accessible and quality health care for women and children is an existing challenge, which is further exacerbated during pandemics. There is a knowledge gap about the effect of pandemics on maternal, newborn, and child well-being. This systematic review was conducted to study maternal and child health (MCH) services utilization during pandemics (Zika, Ebola, and COVID-19) and the effectiveness of various interventions undertaken for ensuring utilization of MCH services.
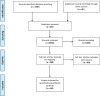
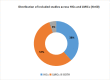
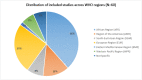
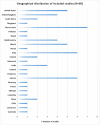
Methodology: A systematic and comprehensive search was conducted in MEDLINE/PubMed, Cochrane CENTRAL, Embase, Epistemonikos, ScienceDirect, and Google Scholar. Of 5643 citations, 60 potential studies were finally included for analysis. The included studies were appraised using JBI Critical appraisal tools. Study selection and data extraction were done independently and in duplicate. Findings are presented narratively based on the RMNCHA framework by World Health Organization (WHO).
Results: Maternal and child health services such as antenatal care (ANC) visits, institutional deliveries, immunization uptake, were greatly affected during a pandemic situation. Innovative approaches in form of health care services through virtual consultation, patient triaging, developing dedicated COVID maternity centers and maternity schools were implemented in different places for ensuring continuity of MCH care during pandemics. None of the studies reported the effectiveness of these interventions during pandemic-related health emergencies.
Conclusion: The findings suggest that during pandemics, MCH care utilization often gets affected. Many innovative interventions were adopted to ensure MCH services. However, they lack evidence about their effectiveness. It is critically important to implement evidence-based appropriate interventions for better MCH care utilization.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Bannon B. Lessons for USAID on the effects of the zika outbreak on mch services: learning from the past to prepare for the future case studies in five latin american and caribbean countries cross-cutting report for dissemination march 2020.
-
- Sahoo KC, Negi S, Patel K, Mishra BK, Palo SK, Pati S. Challenges in Maternal and Child Health Services Delivery and Access during Pandemics or Public Health Disasters in Low-and Middle-Income Countries: A Systematic Review. Healthc (Basel, Switzerland). 2021;9. doi: 10.3390/healthcare9070828 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

