From saliva to SNP: non-invasive, point-of-care genotyping for precision medicine applications using recombinase polymerase amplification and giant magnetoresistive nanosensors
- PMID: 35537344
- PMCID: PMC9156572
- DOI: 10.1039/d2lc00233g
From saliva to SNP: non-invasive, point-of-care genotyping for precision medicine applications using recombinase polymerase amplification and giant magnetoresistive nanosensors
Abstract
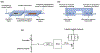
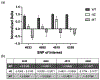
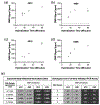
Genetic testing is considered a cornerstone of the precision medicine paradigm. Genotyping of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) has been shown to provide insights into several important issues, including therapy selection and drug responsiveness. However, a scarcity of widely deployable and cost-effective genotyping tools has limited the integration of precision medicine into routine clinical practice. The objective of our work was to develop a portable, cost-effective, and automated platform that performs SNP genotyping at the point-of-care (POC). Using recombinase polymerase amplification (RPA) and giant magnetoresistive (GMR) nanosensors, we present a highly automated and multiplexed point-of-care platform that utilizes direct saliva for the qualitative genotyping of four SNPs (rs4633, rs4680, rs4818, rs6269) along the catechol-O-methyltransferase gene (COMT), which is associated with the modulation of pain sensitivity and perioperative opioid use. Using this approach, we successfully amplify, detect, and genotype all four of the SNPs, demonstrating 100% accordance between the experimental results obtained using the automated RPA and GMR genotyping assay and the results obtained using a COMT PCR genotyping assay that was formerly validated using pyrosequencing. This automated, portable, and multiplexed RPA and GMR assay shows great promise as a solution for SNP genotyping at the POC and reinforces the broad applications of magnetic nanotechnology in biomedicine.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures
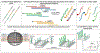

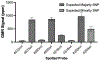

References
-
- Ashley EA, Nat Rev Genet, 2016,17, 507–522. - PubMed
-
- Manolio TA, Chisholm RL, Ozenberger B, Roden DM, Williams MS, Wilson R, Bick D, Bottinger EP, Brilliant MH, Eng C, Frazer KA, Korf B, Ledbetter DH, Lupski JR, Marsh C, Mrazek D, Murray MF, O’Donnell PH, Rader DJ, Relling MV, Shuldiner AR, Valle D, Weinshilboum R, Green ED and Ginsburg GS, Genet Med, 2013, 15, 258–267. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

