Effects of health literacy on type 2 diabetic patients' glycemic control, self-management, and quality of life
- PMID: 35537729
- PMCID: PMC9280600
- DOI: 10.15537/smj.2022.43.5.20210917
Effects of health literacy on type 2 diabetic patients' glycemic control, self-management, and quality of life
Abstract
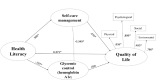
Objectives: To examine the pathway in which health literacy affects diabetic patients' quality of life (QoL) with self-care management skills and glycemic control levels (hemoglobin A1c [HbA1c]) mediating the relationship.
Methods: A cross-sectional study carried out between April 2019 and September 2019. A convenience sample of participants with type 2 diabetes mellitus were recruited from 3 primary healthcare centers, Al Ahsa, Saudi Arabia. Data were collected using structured interviews and HbA1c levels were collected from medical files. Structural equation modeling was also used.
Results: Among the 256 participants, 27.3% had a marginal level of health literacy and 35.5% had an inadequate level of health literacy. Health literacy positively affects self-care management, glycemic control (HbA1c), and QoL directly and indirectly. Self-care management partially mediates this relationship.
Conclusion: Healthcare providers need to assess health literacy and develop interventions that enhance diabetic patients' health literacy because it influences self-care management skills, glycemic control, and patients' QoL. Health literacy should be considered as a key for health education and healthcare encounter to improve health outcomes.
Keywords: diabetes; glycemic control; health literacy; quality of life; self-care management; structural equation modeling.
Copyright: © Saudi Medical Journal.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pathways of empowerment perceptions, health literacy, self-efficacy, and self-care behaviors to glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.Patient Educ Couns. 2016 Feb;99(2):287-94. doi: 10.1016/j.pec.2015.08.021. Epub 2015 Sep 2. Patient Educ Couns. 2016. PMID: 26341940
-
Health literacy, self-efficacy, self-care behaviors, and glycemic control among older adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a cross-sectional study in Thai communities.BMC Geriatr. 2023 May 16;23(1):297. doi: 10.1186/s12877-023-04010-0. BMC Geriatr. 2023. PMID: 37193967 Free PMC article.
-
The association of health literacy with glycemic control in Saudi patients with type 2 diabetes.Saudi Med J. 2019 Jul;40(7):675-680. doi: 10.15537/smj.2019.7.24277. Saudi Med J. 2019. PMID: 31287127 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Health Literacy in Diabetes Knowledge, Self-Care, and Glycemic Control: a Meta-analysis.J Gen Intern Med. 2019 Jun;34(6):1007-1017. doi: 10.1007/s11606-019-04832-y. Epub 2019 Mar 15. J Gen Intern Med. 2019. PMID: 30877457 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The effectiveness of patient activation intervention on type 2 diabetes mellitus glycemic control and self-management behaviors: A systematic review of RCTs.Prim Care Diabetes. 2020 Feb;14(1):12-20. doi: 10.1016/j.pcd.2019.08.009. Epub 2019 Sep 20. Prim Care Diabetes. 2020. PMID: 31543458
Cited by
-
Impact of E-health Literacy on Diabetes Self-Care Activities Among People With Type 2 Diabetes Attending Primary Healthcare Centers in Makkah City, Saudi Arabia: A Cross-Sectional Study, 2025.Cureus. 2025 Jul 15;17(7):e87968. doi: 10.7759/cureus.87968. eCollection 2025 Jul. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40666264 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment and Factors Contributing to the Quality of Life in Diabetes Mellitus Patients: A Cross-Sectional Single-Center Study.Cureus. 2024 Feb 17;16(2):e54359. doi: 10.7759/cureus.54359. eCollection 2024 Feb. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38500939 Free PMC article.
-
The association between health literacy and quality of life of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A cross-sectional study.PLoS One. 2024 Oct 31;19(10):e0312833. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0312833. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39480837 Free PMC article.
-
Eid-al-Fitr festivity and Ramadan fasting attitude among individuals with diabetes from Saudi Arabia and Pakistan: a cross-sectional study.BMJ Open. 2022 Sep 6;12(9):e054902. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2021-054902. BMJ Open. 2022. PMID: 36691119 Free PMC article.
-
The Relationship Between Health Literacy Level and Neuropathic Pain Level in Patients With Diabetic Neuropathy.Cureus. 2023 Jul 7;15(7):e41490. doi: 10.7759/cureus.41490. eCollection 2023 Jul. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37426407 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nutbeam D. The evolving concept of health literacy. Soc Sci Med 2008; 67: 2072–2078. - PubMed
-
- Nutbeam D. Health promotion glossary. Health Promot 1986; 1: 113–127. - PubMed
-
- Coughlin SS, Stewart JL, Young L, Heboyan V, De Leo G.. Health literacy and patient web portals. Int J Med Inform 2018; 113: 43–48. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous