Cardiovascular morbidity and all-cause mortality in patients with retinal vein occlusion: a Danish nationwide cohort study
- PMID: 35537802
- PMCID: PMC10447393
- DOI: 10.1136/bjophthalmol-2022-321225
Cardiovascular morbidity and all-cause mortality in patients with retinal vein occlusion: a Danish nationwide cohort study
Abstract
Background/aims: Associations between retinal vein occlusion (RVO) and subsequent cardiovascular disease (CVD) or mortality have not been evaluated in a recent cohort, after novel therapeutic options have increased referrals for treatment of the condition. We aimed to evaluate overall and subtype-stratified risk of CVD and all-cause mortality following RVO and assess any alterations after the introduction of angiostatic therapy in Denmark in 2011.
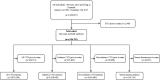
Methods: This nationwide, registry-based cohort study from 1998 to 2018 evaluated 4 194 781 individuals. Hazard ratios (HRs) were reported for RVO as an overall measure and subclassified as branch and central RVO.
Results: Patients with RVO (n=15 665) were median 71.8 years old at the time of exposure and 50.7% were women. RVO associated with incident CVD (adjusted HR 1.13, 95% CI 1.09 to 1.17) but not mortality (adjusted HR 1.00, 95% CI 0.97 to 1.03). Almost similar risks of CVD were found for patients with branch and central RVO (adjusted HRs 1.14, 95% CI 1.03 to 1.25, and 1.12, 95% CI 1.00 to 1.25, respectively), but only patients with central RVO exhibited increased mortality (adjusted HR 1.12, 95% CI 1.04 to 1.21). Risk of CVD, especially non-ischaemic, was higher for patients diagnosed after 2011 (adjusted HRs 1.24, 95% CI 1.15 to 1.33 vs 1.06, 95% CI 1.01 to 1.12).
Conclusion: In a cohort of the Danish population aged 40 years or more, patients with RVO had a 13% increased risk of incident CVD compared with unexposed individuals. Risk of CVD was increased after 2011, when intravitreal angiostatic treatment was introduced and referral practices altered.
Keywords: Epidemiology; Retina.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2023. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: RK have received grants from Novartis Pharma and Senju Pharma, consulting fees from Nanolux and Office future and honoraria for lectures from Bayer within the previous 3 years, none of these directly related to the current work. KHF, LS, PHF, CMJ, SM, TP and JG declares no financial relationships with any organisations that might have an interest in the submitted work in the previous 3 years and no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
