Human cytomegalovirus RNA2.7 inhibits RNA polymerase II (Pol II) Serine-2 phosphorylation by reducing the interaction between Pol II and phosphorylated cyclin-dependent kinase 9 (pCDK9)
- PMID: 35537980
- PMCID: PMC9243627
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virs.2022.02.011
Human cytomegalovirus RNA2.7 inhibits RNA polymerase II (Pol II) Serine-2 phosphorylation by reducing the interaction between Pol II and phosphorylated cyclin-dependent kinase 9 (pCDK9)
Abstract
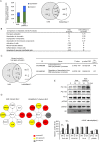
Human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) is a ubiquitous pathogen belongs to betaherpesvirus subfamily. RNA2.7 is a highly conserved long non-coding RNA accounting for more than 20% of total viral transcripts. In our study, functions of HCMV RNA2.7 were investigated by comparison of host cellular transcriptomes between cells infected with HCMV clinical strain and RNA2.7 deleted mutant. It was demonstrated that RNA polymerase II (Pol II)-dependent host gene transcriptions were significantly activated when RNA2.7 was removed during infection. A 145 nt-in-length motif within RNA2.7 was identified to inhibit the phosphorylation of Pol II Serine-2 (Pol II S2) by reducing the interaction between Pol II and phosphorylated cyclin-dependent kinase 9 (pCDK9). Due to the loss of Pol II S2 phosphorylation, cellular DNA pre-replication complex (pre-RC) factors, including Cdt1 and Cdc6, were significantly decreased, which prevented more cells from entering into S phase and facilitated viral DNA replication. Our results provide new insights of HCMV RNA2.7 functions in regulation of host cellular transcription.
Keywords: Cyclin-dependent kinase 9 (CDK9); Human cytomegalovirus (HCMV); Phosphorylation; RNA polymerase II (Pol II); RNA2.7.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Publishing services by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Cyclin T1/CDK9 interacts with influenza A virus polymerase and facilitates its association with cellular RNA polymerase II.J Virol. 2010 Dec;84(24):12619-27. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01696-10. Epub 2010 Oct 13. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 20943989 Free PMC article.
-
Human cytomegalovirus infection induces specific hyperphosphorylation of the carboxyl-terminal domain of the large subunit of RNA polymerase II that is associated with changes in the abundance, activity, and localization of cdk9 and cdk7.J Virol. 2005 Dec;79(24):15477-93. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.24.15477-15493.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 16306619 Free PMC article.
-
The carboxyl-terminal domain of RNA polymerase II is phosphorylated by a complex containing cdk9 and infected-cell protein 22 of herpes simplex virus 1.J Virol. 2005 Jun;79(11):6757-62. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.11.6757-6762.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 15890914 Free PMC article.
-
RNA polymerase II transcription elongation and Pol II CTD Ser2 phosphorylation: A tail of two kinases.Nucleus. 2014 May-Jun;5(3):224-36. doi: 10.4161/nucl.29347. Epub 2014 May 30. Nucleus. 2014. PMID: 24879308 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CDK9 keeps RNA polymerase II on track.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021 Jul;78(14):5543-5567. doi: 10.1007/s00018-021-03878-8. Epub 2021 Jun 19. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 34146121 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Aid or Antagonize: Nuclear Long Noncoding RNAs Regulate Host Responses and Outcomes of Viral Infections.Cells. 2023 Mar 23;12(7):987. doi: 10.3390/cells12070987. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37048060 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human cytomegalovirus RNA2.7 inhibits ferroptosis by upregulating ferritin and GSH via promoting ZNF395 degradation.PLoS Pathog. 2024 Dec 26;20(12):e1012815. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1012815. eCollection 2024 Dec. PLoS Pathog. 2024. PMID: 39724092 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and characterization of human cytomegalovirus-encoded circular RNAs.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Nov 14;12:980974. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.980974. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36452301 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into the Transcriptome of Human Cytomegalovirus: A Comprehensive Review.Viruses. 2023 Aug 8;15(8):1703. doi: 10.3390/v15081703. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 37632045 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

