The Impact of Trimetazidine on Cardiac Fibrosis, Inflammation, and Function in Ischemic Cardiomyopathy Patients
- PMID: 35538296
- PMCID: PMC10516770
- DOI: 10.1007/s10557-022-07340-0
The Impact of Trimetazidine on Cardiac Fibrosis, Inflammation, and Function in Ischemic Cardiomyopathy Patients
Abstract
Background: Previous studies have shown that Trimetazidine (TMZ) improves vascular endothelial function and reduces the inflammatory process progression. However, limited data have been available regarding its effects on myocardial fibrosis following ischemia and causing left ventricular dysfunction.
Purpose: To investigate the impact of TMZ adjuvant therapy for ischemic cardiomyopathy (ICM) on cardiac fibrosis, vascular endothelial function, inflammation, and myocardial functions.
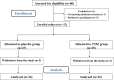
Methods: This randomized, double-blind controlled clinical trial included 48 patients (aged 59.4 ± 9 years) with ICM who were randomly assigned to two groups: TMZ 35 mg twice daily and placebo in addition to conventional ICM medications. All patients received the tablets for 3 months. Both groups were then compared in terms of connective tissue growth factor (CTGF), endothelin-1 (ET-1), tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), and some echocardiographic indices, weekly angina attacks and nitrate consumption before and after treatment.
Results: No significant differences between CTGF, ET-1, and TNF-α levels, in addition to some echocardiographic indices, were observed between both groups before treatment. After treatment, the TMZ group had significantly lower ET-1 than the placebo group, with both groups exhibiting a substantial decrease in TNF-α and CTGF. The TMZ group had lower mean ± SD levels for TNF-α and CTGF and showed significant improvement in echocardiographic indices and weekly angina attacks after treatment.
Conclusion: Adjunctive TMZ therapy for ICM effectively improved vascular endothelial function and reduced inflammation. Furthermore, our exploratory findings may be used to provide new information on the potential effects of TMZ on myocardial fibrosis by downregulating CTGF.
Keywords: Trimetazidine; cardiac fibrosis; inflammatory factors; ischemic cardiomyopathy; vascular endothelial function.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
References
-
- Bhandari B, Rodriguez BSQ, Masood W. Ischemic cardiomyopathy. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island: StatPearls; 2020.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous