Association between baseline body mass index and survival in men with metastatic hormone-sensitive prostate cancer: ECOG-ACRIN CHAARTED E3805
- PMID: 35538398
- PMCID: PMC9839346
- DOI: 10.1002/pros.24369
Association between baseline body mass index and survival in men with metastatic hormone-sensitive prostate cancer: ECOG-ACRIN CHAARTED E3805
Abstract
Background: E3805 (CHAARTED) is a phase 3 trial demonstrating improved survival for men with metastatic hormone-sensitive prostate cancer (mHSPC) randomized to treatment with docetaxel (D) and androgen-deprivation therapy (ADT) versus ADT alone. We assessed the association of baseline body mass index (BMI) and metformin exposure with quality of life (QOL) and prostate cancer outcomes including survival in patients enrolled in the CHAARTED study.
Methods: We performed a posthoc exploratory analysis of the CHAARTED trial of men with mHSPC randomized to treatment with ADT with or without D between 2006 and 2012. Cox proportional hazards models and Kruskal-Wallis test were used to evaluate the association between BMI with QOL and prostate cancer outcomes and between metformin exposure and survival.
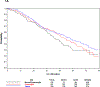
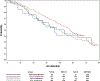
Results: In 788 of 790 enrolled patients with prospectively recorded baseline BMI and metformin exposure status, lower BMI was not associated with survival, but was associated with high volume disease (p < 0.0001) and poorer baseline QOL on functional assessment of cancer therapy-prostate (p = 0.008). Only 68 patients had prevalent metformin exposure at baseline in the CHAARTED trial. Four groups were identified: ADT + D + metformin (n = 39); ADT + D (n = 357); ADT + metformin (n = 29); and ADT alone (n = 363). Baseline clinicopathologic characteristics were similar between groups. In this small exploratory multivariable analysis, metformin exposure was not associated with survival (hazard ratio: 1.15; 95% confidence interval: 0.81-1.63, p = 0.44).
Conclusions: There was no link between baseline BMI and survival, but lower baseline BMI was associated with features of greater cancer burden and poorer QOL.
Keywords: chemohormonal therapy; metabolism; metastatic prostate cancer; quality of life.
© 2022 Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Figures



References
-
- Richards KA, Liou JI, Cryns VL et al. Metformin Use Is Associated with Improved Survival in Patients with Advanced Prostate Cancer on Androgen Deprivation Therapy. J Urol 2018. - PubMed
-
- Chamberlain C, Romundstad P, Vatten L et al. The association of weight gain during adulthood with prostate cancer incidence and survival: a population-based cohort. Int J Cancer 2011; 129: 1199–1206. - PubMed
-
- Wright ME, Chang SC, Schatzkin A et al. Prospective study of adiposity and weight change in relation to prostate cancer incidence and mortality. Cancer 2007; 109: 675–684. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U10 CA027525/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA013650/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA032102/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA233234/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA021076/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA066636/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA189828/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA032102/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA233196/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180794/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180888/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA004919/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA189829/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA004919/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA233320/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA021115/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA031946/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA189974/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA049883/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180821/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA233277/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA107868/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035421/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA233160/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA232760/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA016116/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA233180/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA023318/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA014548/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180820/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA233270/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA233339/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

