Quorum quenching of Streptococcus mutans via the nano-quercetin-based antimicrobial photodynamic therapy as a potential target for cariogenic biofilm
- PMID: 35538403
- PMCID: PMC9088123
- DOI: 10.1186/s12866-022-02544-8
Quorum quenching of Streptococcus mutans via the nano-quercetin-based antimicrobial photodynamic therapy as a potential target for cariogenic biofilm
Abstract
Background: Quorum sensing (QS) system can regulate the expression of virulence factors and biofilm formation in Streptococcus mutans. Antimicrobial photodynamic therapy (aPDT) inhibits quorum quenching (QQ), and can be used to prevent microbial biofilm. We thereby aimed to evaluate the anti-biofilm potency and anti-metabolic activity of nano-quercetin (N-QCT)-mediated aPDT against S. mutans. Also, in silico evaluation of the inhibitory effect of N-QCT on the competence-stimulating peptide (CSP) of S. mutans was performed to elucidate the impact of aPDT on various QS-regulated genes.
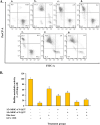
Methods: Cytotoxicity and intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation were assessed following synthesis and confirmation of N-QCT. Subsequently, the minimum biofilm inhibitory concentration (MBIC) of N-QCT against S. mutans and anti-biofilm effects of aPDT were assessed using colorimetric assay and plate counting. Molecular modeling and docking analysis were performed to confirm the connection of QCT to CSP. The metabolic activity of S. mutans and the expression level of various genes involved in QS were evaluated by flow cytometry and reverse transcription quantitative real-time PCR, respectively.
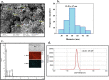
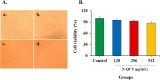
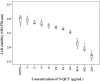
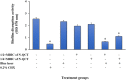
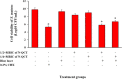
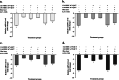
Results: Successful synthesis of non-toxic N-QCT was confirmed through several characterization tests. The MBIC value of N-QCT against S. mutans was 128 μg/mL. Similar to the crystal violet staining, the results log10 CFU/mL showed a significant degradation of preformed biofilms in the group treated with aPDT compared to the control group (P < 0.05). Following aPDT, metabolic activity of S. mutans also decreased by 85.7% (1/2 × MBIC of N-QCT) and 77.3% (1/4 × MBIC of N-QCT), as compared to the control values (P < 0.05). In silico analysis showed that the QCT molecule was located in the site formed by polypeptide helices of CSP. The relative expression levels of the virulence genes were significantly decreased in the presence of N-QCT-mediated aPDT (P < 0.05).
Conclusions: The combination of N-QCT with blue laser as a QQ-strategy leads to maximum ROS generation, disrupts the microbial biofilm of S. mutans, reduces metabolic activity, and downregulates the expression of genes involved in the QS pathway by targeting genes of the QS signaling system of S. mutans.
Keywords: Antimicrobial photodynamic therapy; Competence-stimulating peptide; Dental caries; Quorum sensing; Streptococcus mutans.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
There is no competing interest.
Figures




References
-
- Medapati MR, Singh N, Bhagirath AY, Duan K, Triggs-Raine B, Batista EL, Jr, Chelikani P. Bitter taste receptor T2R14 detects quorum sensing molecules from cariogenic Streptococcus mutans and mediates innate immune responses in gingival epithelial cells. FASEB J. 2021;35(3):e21375. doi: 10.1096/fj.202000208R. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bikash CR, Tal-Gan Y. Identification of highly potent competence stimulating peptide-based quorum sensing activators in Streptococcus mutans through the utilization of N-methyl and reverse alanine scanning. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2019;29(6):811–814. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2019.01.029. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bikash CR, Hamry SR, Tal-Gan Y. Structure–activity relationships of the competence stimulating peptide in Streptococcus mutans reveal motifs critical for membrane protease SepM recognition and ComD receptor activation. ACS Infect Dis. 2018;4(9):1385–1394. doi: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.8b00115. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

