Protease and gag diversity and drug resistance mutations among treatment-naive Mexican people living with HIV
- PMID: 35538426
- PMCID: PMC9088029
- DOI: 10.1186/s12879-022-07446-8
Protease and gag diversity and drug resistance mutations among treatment-naive Mexican people living with HIV
Abstract
Introduction: In Mexico, HIV genotyping is performed in people living with HIV (PLWH) failing their first-line antiretroviral (ARV) regimen; it is not routinely done for all treatment-naive PLWH before ARV initiation. The first nationally representative survey published in 2016 reported that the prevalence of pretreatment drug mutations in treatment-naive Mexican PLWH was 15.5% to any antiretroviral drug and 10.6% to non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NNRTIs) using conventional Sanger sequencing. Most reports in Mexico focus on HIV pol gene and nucleoside and non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NRTI and NNRTI) drug resistance mutations (DRMs) prevalence, using Sanger sequencing, next-generation sequencing (NGS) or both. To our knowledge, NGS has not be used to detect pretreatment drug resistance mutations (DRMs) in the HIV protease (PR) gene and its substrate the Gag polyprotein.
Methods: Treatment-naive adult Mexican PLWH were recruited between 2016 and 2019. HIV Gag and protease sequences were obtained by NGS and DRMs were identified using the WHO surveillance drug resistance mutation (SDRM) list.
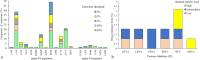
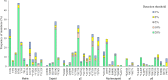
Results: One hundred PLWH attending a public national reference hospital were included. The median age was 28 years-old, and most were male. The median HIV viral load was 4.99 [4.39-5.40] log copies/mL and median CD4 cell count was 150 [68.0-355.78] cells/mm3. As expected, most sequences clustered with HIV-1 subtype B (97.9%). Major PI resistance mutations were detected: 8 (8.3%) of 96 patients at a detection threshold of 1% and 3 (3.1%) at a detection threshold of 20%. A total of 1184 mutations in Gag were detected, of which 51 have been associated with resistance to PI, most of them were detected at a threshold of 20%. Follow-up clinical data was available for 79 PLWH at 6 months post-ART initiation, seven PLWH failed their first ART regimen; however no major PI mutations were identified in these individuals at baseline.
Conclusions: The frequency of DRM in the HIV protease was 7.3% at a detection threshold of 1% and 3.1% at a detection threshold of 20%. NGS-based HIV drug resistance genotyping provide improved detection of DRMs. Viral load was used to monitor ARV response and treatment failure was 8.9%.
Keywords: Antiretroviral therapy; Gag; HIV drug resistance mutations; HIV genotyping; Human immunodeficiency virus; Next generation sequencing; Protease.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Added Value of Next Generation over Sanger Sequencing in Kenyan Youth with Extensive HIV-1 Drug Resistance.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Dec 21;10(6):e0345422. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.03454-22. Epub 2022 Nov 29. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 36445146 Free PMC article.
-
Drug Resistance Mutations in a Population Before Antiretroviral Therapy Initiation in Northern South Africa.AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2022 Mar;38(3):248-256. doi: 10.1089/AID.2021.0026. Epub 2021 Jul 12. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2022. PMID: 34107774
-
Diversity of HIV-1 Subtypes and Transmitted Drug-resistance Mutations Among Minority HIV-1 Variants in a Turkish Cohort.Curr HIV Res. 2022;20(1):54-62. doi: 10.2174/1570162X19666211119111740. Curr HIV Res. 2022. PMID: 34802406
-
Study of the impact of HIV genotypic drug resistance testing on therapy efficacy.Verh K Acad Geneeskd Belg. 2001;63(5):447-73. Verh K Acad Geneeskd Belg. 2001. PMID: 11813503 Review.
-
Prevalence of acquired and transmitted HIV drug resistance in Iran: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Infect Dis. 2024 Jan 2;24(1):29. doi: 10.1186/s12879-023-08916-3. BMC Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 38166733 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
HIV-1 Low-Frequency Variants Identified in Antiretroviral-Naïve Subjects with Virologic Failure after 12 Months of Follow-Up in Panama.Infect Dis Rep. 2023 Aug 1;15(4):436-444. doi: 10.3390/idr15040044. Infect Dis Rep. 2023. PMID: 37623048 Free PMC article.
-
HIV-1 Drug Resistance Detected by Next-Generation Sequencing among ART-Naïve Individuals: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Viruses. 2024 Feb 2;16(2):239. doi: 10.3390/v16020239. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 38400015 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic diversity in the partial sequence of the HIV-1 gag gene among people living with multidrug-resistant HIV-1 infection.Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo. 2024 Jun 7;66:e35. doi: 10.1590/S1678-9946202466035. eCollection 2024. Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo. 2024. PMID: 38865573 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dirección General de Epidemiología de Enfermedades Transmisibles. Secretaria de Salud. Informe Histórico De VIH 2Do Trimestre 2021. Sistema de Vigilancia Epidemiológica de VIH. [Internet]. 2021 https://www.gob.mx/cms/uploads/attachment/file/667817/VIH-Sida_2doTrim_2.... Accessed 13 Sep 2021.
-
- CENSIDA, Secretaría de Salud. Boletín de atención integral de personas que viven con VIH. [Internet]. 2021. https://www.gob.mx/cms/uploads/attachment/file/670963/Bol_DAI_Vol7_N3_SE.... Accessed 13 Sep 2021.
-
- Centro Nacional para la Prevención y Control del VIH y el sida. Guía de manejo antirretroviral de las personas con VIH. [Internet]. 2021. p. 1–279. https://www.gob.mx/cms/uploads/attachment/file/670762/Guia_ARV_2021.pdf. Accessed 13 Jul 2021.
-
- World Health Organization. HIV Drug Resistance Report 2019 [Internet]. WHO. 2019. p. 68. http://www.who.int/hiv/pub/drugresistance/hivdr-report-2019/en/%0A; http://scholar.google.com/scholar/Who.hiv.drug.resistance.report.2012. Accessed 16 Jul 2021.
-
- Haile-Selassie H. Hiv drug resistance report 2017. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2017. p. 68.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

