mRNA expression of toll-like receptors 3, 7, 8, and 9 in the nasopharyngeal epithelial cells of coronavirus disease 2019 patients
- PMID: 35538443
- PMCID: PMC9086663
- DOI: 10.1186/s12879-022-07437-9
mRNA expression of toll-like receptors 3, 7, 8, and 9 in the nasopharyngeal epithelial cells of coronavirus disease 2019 patients
Abstract
Background: The etiopathogenesis of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) stem partially from the abnormal activation of the innate and adaptive immune systems. Here in the current investigation, the mRNA expression levels of toll-like receptors (TLRs) were evaluated in the nasopharyngeal epithelial cells from COVID-19 patients.
Methods: Epithelial cells were obtained using nasopharyngeal swab samples from 90 COVID-19 patients and 50 controls. COVID-19 cases were classified into those without symptoms, with symptoms but not hospitalized, and with symptoms and hospitalized. To determine the mRNA expression levels of TLRs, first RNA was extracted and cDNA was synthesized, and finally Real-time PCR was exerted.
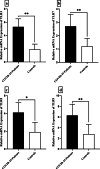
Results: It was seen that the transcript levels of TLR3, TLR7, TLR8, and TLR9 were overexpressed in the COVID-19 patients with clinical symptoms needing hospitalization as well as in those with clinical symptoms without needing for hospitalization compared to controls. Upregulation of TLRs was associated with clinical presentations of the patients.
Conclusions: Modulation of TLR3, TLR7, TLR8, TLR9 in the epithelial cells of COVID-19 cases may estimate the disease severity and requirement for hospitalization.
Keywords: Coronavirus disease 2019; Epithelial cell; Inflammation; Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2; Toll-like receptor.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nasopharyngeal epithelial cells from patients with coronavirus disease 2019 express abnormal levels of Toll-like receptors.Pathog Glob Health. 2023 Jun;117(4):401-408. doi: 10.1080/20477724.2023.2166378. Epub 2023 Jan 18. Pathog Glob Health. 2023. PMID: 36651678 Free PMC article.
-
Transcript levels of Toll-Like Receptors 5, 8 and 9 correlate with inflammatory activity in Ulcerative Colitis.BMC Gastroenterol. 2011 Dec 20;11:138. doi: 10.1186/1471-230X-11-138. BMC Gastroenterol. 2011. PMID: 22185629 Free PMC article.
-
Expression and distribution of Toll-like receptors in the brain during murine neurocysticercosis.J Neuroimmunol. 2006 Dec;181(1-2):46-56. doi: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2006.07.019. Epub 2006 Sep 29. J Neuroimmunol. 2006. PMID: 17011049 Free PMC article.
-
Differential Expression Patterns of Toll-like Receptors in COVID-19 Patients.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2023 Nov 28;28(11):307. doi: 10.31083/j.fbl2811307. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2023. PMID: 38062845 Review.
-
TLRs: Innate Immune Sentries against SARS-CoV-2 Infection.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 29;24(9):8065. doi: 10.3390/ijms24098065. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37175768 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Role of TLRs in HIV-1 Infection and Potential of TLR Agonists in HIV-1 Vaccine Development and Treatment Strategies.Pathogens. 2023 Jan 5;12(1):92. doi: 10.3390/pathogens12010092. Pathogens. 2023. PMID: 36678440 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Self-DNA driven inflammation in COVID-19 and after mRNA-based vaccination: lessons for non-COVID-19 pathologies.Front Immunol. 2024 Feb 19;14:1259879. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1259879. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38439942 Free PMC article.
-
Changes of GH-IGFs and its relationship with growth retardation in children with bronchial asthma.Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2024 May 15;79:100385. doi: 10.1016/j.clinsp.2024.100385. eCollection 2024. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2024. PMID: 38754227 Free PMC article.
-
The relationship between chronic immune response and neurodegenerative damage in long COVID-19.Front Immunol. 2022 Dec 16;13:1039427. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1039427. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36591299 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nasopharyngeal epithelial cells from patients with coronavirus disease 2019 express abnormal levels of Toll-like receptors.Pathog Glob Health. 2023 Jun;117(4):401-408. doi: 10.1080/20477724.2023.2166378. Epub 2023 Jan 18. Pathog Glob Health. 2023. PMID: 36651678 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Organization WH: Clinical management of severe acute respiratory infection (SARI) when COVID-19 disease is suspected: interim guidance, 13 March 2020. In.: World Health Organization; 2020.
-
- Mohammadhosayni M, Mohammadi FS, Ezzatifar F, Gorabi AM, Khosrojerdi A, Aslani S, Hemmatzadeh M, Yazdani S, Arabi M, Marofi F. Matrix metalloproteinases are involved in the development of neurological complications in patients with Coronavirus disease 2019. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021;100:108076. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2021.108076. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous