mRNA expression of toll-like receptors 3, 7, 8, and 9 in the nasopharyngeal epithelial cells of coronavirus disease 2019 patients
- PMID: 35538443
- PMCID: PMC9086663
- DOI: 10.1186/s12879-022-07437-9
mRNA expression of toll-like receptors 3, 7, 8, and 9 in the nasopharyngeal epithelial cells of coronavirus disease 2019 patients
Abstract
Background: The etiopathogenesis of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) stem partially from the abnormal activation of the innate and adaptive immune systems. Here in the current investigation, the mRNA expression levels of toll-like receptors (TLRs) were evaluated in the nasopharyngeal epithelial cells from COVID-19 patients.
Methods: Epithelial cells were obtained using nasopharyngeal swab samples from 90 COVID-19 patients and 50 controls. COVID-19 cases were classified into those without symptoms, with symptoms but not hospitalized, and with symptoms and hospitalized. To determine the mRNA expression levels of TLRs, first RNA was extracted and cDNA was synthesized, and finally Real-time PCR was exerted.
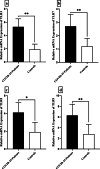
Results: It was seen that the transcript levels of TLR3, TLR7, TLR8, and TLR9 were overexpressed in the COVID-19 patients with clinical symptoms needing hospitalization as well as in those with clinical symptoms without needing for hospitalization compared to controls. Upregulation of TLRs was associated with clinical presentations of the patients.
Conclusions: Modulation of TLR3, TLR7, TLR8, TLR9 in the epithelial cells of COVID-19 cases may estimate the disease severity and requirement for hospitalization.
Keywords: Coronavirus disease 2019; Epithelial cell; Inflammation; Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2; Toll-like receptor.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Organization WH: Clinical management of severe acute respiratory infection (SARI) when COVID-19 disease is suspected: interim guidance, 13 March 2020. In.: World Health Organization; 2020.
-
- Mohammadhosayni M, Mohammadi FS, Ezzatifar F, Gorabi AM, Khosrojerdi A, Aslani S, Hemmatzadeh M, Yazdani S, Arabi M, Marofi F. Matrix metalloproteinases are involved in the development of neurological complications in patients with Coronavirus disease 2019. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021;100:108076. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2021.108076. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous