The effect of concurrent use of swaddle and sucrose on the intensity of pain during venous blood sampling in neonate: a clinical trial study
- PMID: 35538448
- PMCID: PMC9087931
- DOI: 10.1186/s12887-022-03323-0
The effect of concurrent use of swaddle and sucrose on the intensity of pain during venous blood sampling in neonate: a clinical trial study
Abstract
Background & objective: Infants undergo painful procedures while receiving care and treatment. Blood sampling is the most common painful procedure for infants. Pain control plays a significant role in preventing unwanted physical and psychological effects. Therefore, this study aimed to investigate the effect of concurrent use of swaddle and sucrose taste on the pain intensity during venous blood sampling in neonates.
Methods: In this clinical trial study, 60 infants admitted to the neonatal ward of Amirkola Hospital were randomly divided into four groups of 15 patients. In the first group, the infants were swaddled before blood sampling. In the second group, sucrose was administered to infants. In the third group, the neonates were swaddled and given sucrose simultaneously, and in the fourth group (control), blood sampling was performed routinely. PIPP pain scale and demographic questionnaire were used to collect the data. Data analysis was performed using SPSS23.
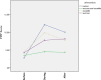
Results: The results showed a significant difference between the mean pain intensity in neonates in the sucrose-swaddle group (4.53 ± 1.30) and the sucrose (7.73 ± 2.73), swaddle (9.86 ± 33.33), and control (12.13 ± 2.06) groups during blood sampling (P < 0.001). Besides, after blood sampling, there was a significant difference between the mean pain intensity in neonates in the sucrose-swaddle group (4.33 ± 1.23) and the sucrose (8.13 ± 2.66), swaddle (7.73 ± 2.78), and control (10.00. ± 1.96) groups (P < 0.001).
Conclusion: The present study showed that pain severity during and after venous blood sampling was lower in the swaddle-sucrose group than in other groups. Therefore, it is recommended that the combined method of swaddle-sucrose be used in infants as a better pain reliever when intravenous blood sampling is performed.
Keywords: Blood sampling; Clinical trial; Infant; Pain management; Sucrose; Swaddle.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of eye shield and ear muffs on pain intensity during venous blood sampling in premature infants: a clinical trial study.BMC Pediatr. 2023 Apr 6;23(1):161. doi: 10.1186/s12887-023-03978-3. BMC Pediatr. 2023. PMID: 37024882 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The effect of combined non-pharmacological interventions on venous blood sampling pain in preterm infants: a clinical trial study.BMC Pediatr. 2025 Apr 3;25(1):273. doi: 10.1186/s12887-025-05626-4. BMC Pediatr. 2025. PMID: 40181237 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Comparison of the analgesic effect of oral sucrose and/or music in preterm neonates: A double-blind randomized clinical trial.Complement Ther Med. 2020 Jan;48:102271. doi: 10.1016/j.ctim.2019.102271. Epub 2019 Nov 27. Complement Ther Med. 2020. PMID: 31987233 Clinical Trial.
-
Oral sucrose and pain relief for preterm infants.Pain Manag Nurs. 2003 Jun;4(2):62-9. doi: 10.1016/s1524-9042(02)54201-6. Pain Manag Nurs. 2003. PMID: 12836150 Review.
-
How painful is a heelprick or a venipuncture in a newborn?J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2016;29(2):202-6. doi: 10.3109/14767058.2014.992334. Epub 2014 Dec 23. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2016. PMID: 25534000 Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of eye shield and ear muffs on pain intensity during venous blood sampling in premature infants: a clinical trial study.BMC Pediatr. 2023 Apr 6;23(1):161. doi: 10.1186/s12887-023-03978-3. BMC Pediatr. 2023. PMID: 37024882 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Frequency and pain intensity of painful procedures in premature infants hospitalized in the neonatal intensive care unit.J Educ Health Promot. 2024 Dec 28;13:467. doi: 10.4103/jehp.jehp_1042_24. eCollection 2024. J Educ Health Promot. 2024. PMID: 39850281 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of combined non-pharmacological interventions on venous blood sampling pain in preterm infants: a clinical trial study.BMC Pediatr. 2025 Apr 3;25(1):273. doi: 10.1186/s12887-025-05626-4. BMC Pediatr. 2025. PMID: 40181237 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Non-pharmacological management of infant and young child procedural pain.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Jun 14;6(6):CD006275. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006275.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 37314064 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Verklan MT, Walden M, Forest S. Core curriculum for neonatal intensive care nursing e-book. Elsevier Health Sciences; 2020.
-
- ArefNejad M, Jaberi N, Khalilipour E, Isfahani P. Survey of neonatal mortality in nicu in Amiralmomenin Hospital of Zabol University of Medical Sciences in 2014: A short report. J Rafsanjan Univ Med Sci. 2016;15(1):91–98.
-
- Dames LJP, Alves VH, Rodrigues DP, de Souza RRB, Medeiros FVA, Paiva ED. Nurses’ practical knowledge on the clinical management of neonatal pain: a descriptive study. Online Braz J Nurs. 2016;15(3):393–403. doi: 10.17665/1676-4285.20165413. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical