N6-methyladenosine-modified TRAF1 promotes sunitinib resistance by regulating apoptosis and angiogenesis in a METTL14-dependent manner in renal cell carcinoma
- PMID: 35538475
- PMCID: PMC9087993
- DOI: 10.1186/s12943-022-01549-1
N6-methyladenosine-modified TRAF1 promotes sunitinib resistance by regulating apoptosis and angiogenesis in a METTL14-dependent manner in renal cell carcinoma
Abstract
Background: Sunitinib resistance can be classified into primary and secondary resistance. While accumulating research has indicated several underlying factors contributing to sunitinib resistance, the precise mechanisms in renal cell carcinoma are still unclear.
Methods: RNA sequencing and m6A sequencing were used to screen for functional genes involved in sunitinib resistance. In vitro and in vivo experiments were carried out and patient samples and clinical information were obtained for clinical analysis.
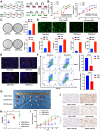
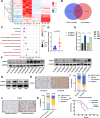
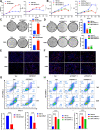
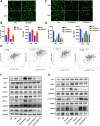
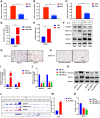
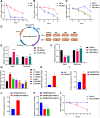
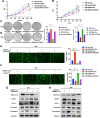
Results: We identified a tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor, TRAF1, that was significantly increased in sunitinib-resistant cells, resistant cell-derived xenograft (CDX-R) models and clinical patients with sunitinib resistance. Silencing TRAF1 increased sunitinib-induced apoptotic and antiangiogenic effects. Mechanistically, the upregulated level of TRAF1 in sunitinib-resistant cells was derived from increased TRAF1 RNA stability, which was caused by an increased level of N6-methyladenosine (m6A) in a METTL14-dependent manner. Moreover, in vivo adeno-associated virus 9 (AAV9) -mediated transduction of TRAF1 suppressed the sunitinib-induced apoptotic and antiangiogenic effects in the CDX models, whereas knockdown of TRAF1 effectively resensitized the sunitinib-resistant CDXs to sunitinib treatment.
Conclusions: Overexpression of TRAF1 promotes sunitinib resistance by modulating apoptotic and angiogenic pathways in a METTL14-dependent manner. Targeting TRAF1 and its pathways may be a novel pharmaceutical intervention for sunitinib-treated patients.
Keywords: METTL14; N6-methyladenosine; RCC; Sunitinib-resistance; TRAF1.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Nerich V, Hugues M, Paillard MJ, Borowski L, Nai T, Stein U, Nguyen Tan Hon T. Montcuquet P, Maurina T, Mouillet G, et al. Clinical impact of targeted therapies in patients with metastatic clear-cell renal cell carcinoma. Onco Targets Ther. 2014;7:365–374. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S56370. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

