Construction of an individualized clinical prognostic index based on ubiquitination-associated lncRNA in clear cell renal cell carcinoma patients
- PMID: 35538487
- PMCID: PMC9087998
- DOI: 10.1186/s12957-022-02618-x
Construction of an individualized clinical prognostic index based on ubiquitination-associated lncRNA in clear cell renal cell carcinoma patients
Abstract
Background: ccRCC is considered as the main subtype of RCC, which accounted for sixth deadliest cancer worldwide. Recently, ubiquitination has been reported to be closely involved in the progression of tumore. The purpose of this study was to identify the ubiquitination-associated genes and co-expressed lncRNAs on the prognosis of clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) patients.
Methods and patients: We downloaded 530 cases and the corresponding transcriptome profiling from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database. We distinguished mRNA and lncRNA expression data from the transcriptome profiling and then extracted the expression of mRNAs that regulate protein ubiquitination. We obtained lncRNAs associated with protein ubiquitination regulation from the lncRNA data by gene co-expression analysis. Cox regression analysis of survival time, survival status, and lncRNA expression level was carried out, and a prognostic index (PI) was constructed.
Results: The PI was established based on 8 prognostic lncRNAs that regulate protein ubiquitination and distinguish the high-risk group patients from all patients. Multivariate analysis indicated that this PI was an individualized clinical prognostic factor for patients with ccRCC. Regarding clinical characteristics, a ubiquitination-associated clinical-prognostic index (UCPI), containing 8 ubiquitination-related lncRNAs and age, was established and tested with AUC of 0.80.
Conclusion: We established a UCPI containing 8 lncRNAs related to protein ubiquitination. This UCPI may become an appropriate model to predict the prognosis in ccRCC patients and guide clinicians to adjust the follow-up regimen.
Keywords: Bioinformatic analysis; Clear cell renal cell carcinoma; Clinical-prognostic index; Long noncoding RNA; Ubiquitination.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
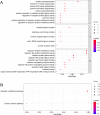

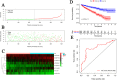
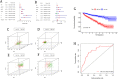
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

