Myt1l haploinsufficiency leads to obesity and multifaceted behavioral alterations in mice
- PMID: 35538503
- PMCID: PMC9087967
- DOI: 10.1186/s13229-022-00497-3
Myt1l haploinsufficiency leads to obesity and multifaceted behavioral alterations in mice
Abstract
Background: The zinc finger domain containing transcription factor Myt1l is tightly associated with neuronal identity and is the only transcription factor known that is both neuron-specific and expressed in all neuronal subtypes. We identified Myt1l as a powerful reprogramming factor that, in combination with the proneural bHLH factor Ascl1, could induce neuronal fate in fibroblasts. Molecularly, we found it to repress many non-neuronal gene programs, explaining its supportive role to induce and safeguard neuronal identity in combination with proneural bHLH transcriptional activators. Moreover, human genetics studies found MYT1L mutations to cause intellectual disability and autism spectrum disorder often coupled with obesity.
Methods: Here, we generated and characterized Myt1l-deficient mice. A comprehensive, longitudinal behavioral phenotyping approach was applied.
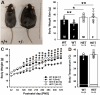
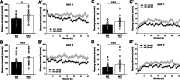
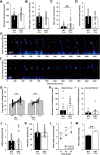
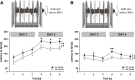
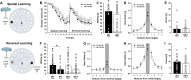
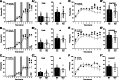
Results: Myt1l was necessary for survival beyond 24 h but not for overall histological brain organization. Myt1l heterozygous mice became increasingly overweight and exhibited multifaceted behavioral alterations. In mouse pups, Myt1l haploinsufficiency caused mild alterations in early socio-affective communication through ultrasonic vocalizations. In adulthood, Myt1l heterozygous mice displayed hyperactivity due to impaired habituation learning. Motor performance was reduced in Myt1l heterozygous mice despite intact motor learning, possibly due to muscular hypotonia. While anxiety-related behavior was reduced, acoustic startle reactivity was enhanced, in line with higher sensitivity to loud sound. Finally, Myt1l haploinsufficiency had a negative impact on contextual fear memory retrieval, while cued fear memory retrieval appeared to be intact.
Limitations: In future studies, additional phenotypes might be identified and a detailed characterization of direct reciprocal social interaction behavior might help to reveal effects of Myt1l haploinsufficiency on social behavior in juvenile and adult mice.
Conclusions: Behavioral alterations in Myt1l haploinsufficient mice recapitulate several clinical phenotypes observed in humans carrying heterozygous MYT1L mutations and thus serve as an informative model of the human MYT1L syndrome.
Keywords: Autism; Obesity; Social behavior; Transcription factor; Ultrasonic vocalization.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
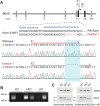
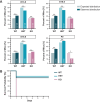
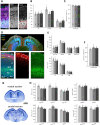

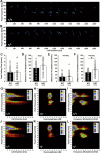

Similar articles
-
A survey of hypothalamic phenotypes identifies molecular and behavioral consequences of MYT1L haploinsufficiency in male and female mice.Horm Behav. 2025 Jul 28;174:105796. doi: 10.1016/j.yhbeh.2025.105796. Online ahead of print. Horm Behav. 2025. PMID: 40729938
-
A survey of hypothalamic phenotypes identifies molecular and behavioral consequences of MYT1L haploinsufficiency in male and female mice.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Nov 25:2024.11.25.625294. doi: 10.1101/2024.11.25.625294. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Horm Behav. 2025 Jul 28;174:105796. doi: 10.1016/j.yhbeh.2025.105796. PMID: 39651298 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Methylphenidate for children and adolescents with autism spectrum disorder.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Nov 21;11(11):CD011144. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011144.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 29159857 Free PMC article.
-
Short-Term Memory Impairment.2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 31424720 Free Books & Documents.
-
Memantine for autism spectrum disorder.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Aug 25;8(8):CD013845. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013845.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36006807 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Genome-Wide Structural Variation Analysis and Breed Comparison of Local Domestic Ducks in Shandong Province, China.Animals (Basel). 2024 Dec 18;14(24):3657. doi: 10.3390/ani14243657. Animals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39765561 Free PMC article.
-
Lifespan in rodents with MYT1L heterozygous mutation.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2024 Dec 17:rs.3.rs-5140229. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-5140229/v1. Res Sq. 2024. Update in: Sci Rep. 2025 Feb 10;15(1):4998. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-88462-x. PMID: 39764117 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Stimulus-Dependent Expression of Bdnf Is Mediated by ATF2, MYT1L, and EGR1 Transcription Factors.J Neurosci. 2025 Mar 19;45(12):e0313242025. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0313-24.2025. J Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 39947922
-
Chromosomal and gonadal sex have differing effects on social motivation in mice.Biol Sex Differ. 2025 Feb 19;16(1):13. doi: 10.1186/s13293-025-00690-y. Biol Sex Differ. 2025. PMID: 39966983 Free PMC article.
-
Autism- and intellectual disability-associated MYT1L mutation alters human cortical interneuron differentiation, maturation, and physiology.Stem Cell Reports. 2025 Mar 11;20(3):102421. doi: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2025.102421. Epub 2025 Feb 27. Stem Cell Reports. 2025. PMID: 40020682 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Blanchet P, Bebin M, Bruet S, Cooper GM, Thompson ML, Duban-Bedu B, Gerard B, Piton A, Suckno S, Deshpande C, Clowes V, Vogt J, Turnpenny P, Williamson MP, Alembik Y. MYT1L mutations cause intellectual disability and variable obesity by dysregulating gene expression and development of the neuroendocrine hypothalamus. PLoS Genet. 2017;13(8):e1006957. 10.1371/journal.pgen.1006957. - PMC - PubMed
-
- De Rocker N, Vergult S, Koolen D, Jacobs E, Hoischen A, Zeesman S, Bang B, Béna F, Bockaert N, Bongers EM, deRavel T, Devriendt K, Giglio S, Faivre L, Joss S, Maas S, Marle N, Novara F, Nowaczyk MJ, Peeters H, Polstra A, Roelens F, Rosenberg C, Thevenon J, Tümer Z, Vanhauwaert S, Varvagiannis K, Willaert A, Willemsen M, Willems M, Zuffardi O, Coucke P, Speleman F, Eichler EE, Kleefstra T, Menten B. Refinement of the critical 2p25.3 deletion region: the role of MYT1L in intellectual disability and obesity. Genet Med. 2015;17(6):460–6. 10.1038/gim.2014.124. - PubMed
-
- Stevens SJ, van Ravenswaaij-Arts CM, Janssen JW, Klein Wassink-Ruiter JS, van Essen AJ, Dijkhuizen T, van Rheenen J, Heuts-Vijgen R, Stegmann AP, Smeets EE, Engelen JJ. MYT1L is a candidate gene for intellectual disability in patients with 2p25.3 (2pter) deletions. Am J Med Genet A. 2011;155A(11):2739–45. 10.1002/ajmg.a.34274. - PubMed
-
- Windheuser IC, Becker J, Cremer K, Hundertmark H, Yates LM, Mangold E, Peters S, Degenhardt F, Ludwig KU, Zink AM, Lessel D, Bierhals T, Herget T, Johannsen J, Denecke J, Wohlleber E, Strom TM, Wieczorek D, Bertoli M, Colombo R, Hempel M, Engels H. Nine newly identified individuals refine the phenotype associated with MYT1L mutations. Am J Med Genet A. 2020;182(5):1021–31. 10.1002/ajmg.a.61515. - PubMed
-
- Satterstrom FK, Kosmicki JA, Wang J, Breen MS, De Rubeis S, An JY, Peng M, Collins R, Grove J, Klei L, Stevens C, Reichert J, Mulhern MS, Artomov M, Gerges S, Sheppard B, Xu X, Bhaduri A, Norman U, Brand H, Schwartz G, Nguyen R, Guerrero EE, Dias C; Autism Sequencing Consortium; iPSYCH-Broad Consortium, Betancur C, Cook EH, Gallagher L, Gill M, Sutcliffe JS, Thurm A, Zwick ME, Børglum AD, State MW, Cicek AE, Talkowski ME, Cutler DJ, Devlin B, Sanders SJ, Roeder K, Daly MJ, Buxbaum JD. Large-Scale Exome Sequencing Study Implicates Both Developmental and Functional Changes in the Neurobiology of Autism. Cell. 2020;180(3):568–584.e23. 10.1016/j.cell.2019.12.036. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

