Interaction of MC4R rs17782313 variants and dietary carbohydrate quantity and quality on basal metabolic rate and general and central obesity in overweight/obese women: a cross-sectional study
- PMID: 35538513
- PMCID: PMC9092846
- DOI: 10.1186/s12902-022-01023-5
Interaction of MC4R rs17782313 variants and dietary carbohydrate quantity and quality on basal metabolic rate and general and central obesity in overweight/obese women: a cross-sectional study
Abstract
Background: Recent studies have shown that dietary carbohydrate quantity and quality as well as genetic variants may contribute to determining the metabolic rate and general and central obesity. This study aimed to examine interactions between melanocortin 4 receptor gene (MC4R) rs17782313 and dietary carbohydrate intake, glycemic index (GI), and glycemic load (GL) on body mass index (BMI), waist circumferences (WC), basal metabolic rate (BMR), and BMR/kg in overweight/obese women.
Methods: A total of 282 Iranian women (BMI ≥ 25) aged 18-56 years were enrolled in this cross-sectional study. All participants were assessed for blood parameters, body composition, BMR, and dietary intake. Dietary carbohydrate intake, GI, and GL were determined using a valid, reliable 147-item food frequency questionnaire. MC4R rs17782313 was genotyped by the restriction fragment length polymorphism (PCR-RFLP) method.
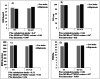
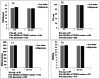
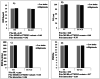
Results: After adjustment for age and energy intake, significant interactions were observed between carbohydrate intake and MC4R rs17782313 in terms of BMI (P Interaction = 0.007), WC (P Interaction = 0.02), and BMR/kg (P Interaction = 0.003) in this way that higher carbohydrate intake, compared with lower intake, was associated with an increase in BMI and WC for individuals with C allele carriers (TC + CC genotypes), while related to an increase in BMR/kg for those carrying the TT genotype. No significant interaction was found between MC4R rs17782313 and GI and GL on BMI, WC, BMR/kg, and BMR.
Conclusions: Interactions between the MC4R rs17782313 and carbohydrate intake probably can have an effect on BMI, WC, and BMR/kg in overweight/obese women.
Keywords: Basal metabolic rate; Carbohydrate; Gene–diet interaction; Glycemic index; Glycemic load; Melanocortin 4 receptor.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
This is formally to submit the article entitled “Interaction of MC4R rs17782313 variants and dietary carbohydrate quantity and quality on basal metabolic rate and general and central obesity in overweight/obese women: a cross-sectional study” prepared by the Tehran University of Medical Sciences for review and, hopefully, publication in your prestigious journal. The authors would like to advise that all authors listed have contributed to the work. All authors have agreed to submit the manuscript to
All authors declared that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Askarpour M, Alizadeh S, Hadi A, Symonds ME, Miraghajani M, Sheikhi A, et al. Effect of Bariatric Surgery on the Circulating Level of Adiponectin, Chemerin, Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor-1, Leptin, Resistin, and Visfatin: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Horm Metab Res. 2020;52(04):207–15. doi: 10.1055/a-1129-6785. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Askarpour M, Khani D, Sheikhi A, Ghaedi E, Alizadeh S. Effect of bariatric surgery on serum inflammatory factors of obese patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes Surg. 2019;29(8):2631–47. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

