Value of lymphadenectomy in patients with surgically resected pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors
- PMID: 35538535
- PMCID: PMC9088076
- DOI: 10.1186/s12893-022-01595-y
Value of lymphadenectomy in patients with surgically resected pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors
Abstract
Background: Although some factors that predict the prognosis in pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor (pNET) have been confirmed, the predictive value of lymph node metastasis (LNM) in the prognosis of pNETs remains conflicting and it is not clear whether regional lymphadenectomy should be performed in all grades of tumors.
Methods: We included pNET patients undergoing surgery in Shanghai pancreatic cancer institute (SHPCI). The risk factors for survival were investigated by the Kaplan-Meier method and Cox regression model. We evaluated the predictors of LNM using Logistic regression.
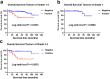
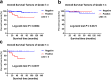
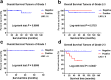
Results: For 206 patients in the SHPCI series, LNM was an independent prognostic factor for entire cohort suggested by multivariate Cox regression analysis. LNM (P = 0.002) predicted poorer overall survival (OS) in grade 2/3 cohort, but there is no significant association between LNM and OS in grade 1 cohort. Grade (P < 0.001) and size (P = 0.049) predicted LNM in entire cohort. Grade (P = 0.002) predicted LNM while regardless of size in grade 2/3 cohort.
Conclusions: Based on our own retrospective data obtained from a single center series, LNM seems to be associated with poorer outcome for patients with grade 2/3 and/or grade 1 > 4 cm tumors. On the other way, LNM was seems to be not associated with prognosis in patients with grade 1 tumors less than 4 cm. Moreover, tumor grade and tumor size seem to act as independent predictors of LNM. Thus, regional lymphadenectomy should be performed in grade 2/3 patients but was not mandatory in grade 1 tumors < 4 cm. It is reasonable to perform functional sparing surgery for grade 1 patients or propose a clinical-radiological monitoring.
Keywords: Lymph node metastasis; Lymphadenectomy; Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Falconi M, Eriksson B, Kaltsas G, Bartsch DK, Capdevila J, Caplin M, et al. ENETS consensus guidelines update for the management of patients with functional pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors and non-functional pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. Neuroendocrinology. 2016;103(2):153–171. doi: 10.1159/000443171. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 81871950/National Natural Science Foundation of China,China
- 81972725/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 21JC1401500/Shanghai Municipal Science and Technology Major Project
- 2019-01-07-00-07-E00057/Scientific Innovation Project of Shanghai Education Committee
- SHDC2020CR1006A/Clinical Research Plan of Shanghai Hospital Development Center
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

