Nicotinamide mononucleotide ameliorates acute lung injury by inducing mitonuclear protein imbalance and activating the UPRmt
- PMID: 35538652
- PMCID: PMC9379602
- DOI: 10.1177/15353702221094235
Nicotinamide mononucleotide ameliorates acute lung injury by inducing mitonuclear protein imbalance and activating the UPRmt
Abstract
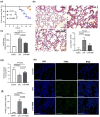
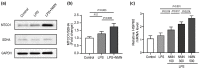
Mitochondria need to interact with the nucleus under homeostasis and stress to maintain cellular demands and nuclear transcriptional programs. Disrupted mitonuclear interaction is involved in many disease processes. However, the role of mitonuclear signaling regulators in endotoxin-induced acute lung injury (ALI) remains unknown. Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) is closely related to mitonuclear interaction with its central role in mitochondrial metabolism. In the current study, C57BL/6J mice were administrated with lipopolysaccharide 15 mg/kg to induce endotoxin-induced ALI and investigated whether the NAD+ precursor nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) could preserve mitonuclear interaction and alleviate ALI. After pretreatment with NMN for 7 days, NAD+ levels in the mitochondrial, nucleus, and total intracellular were significantly increased in endotoxemia mice. Moreover, supplementation of NMN alleviated lung pathologic injury, reduced ROS levels, increased MnSOD activities, mitigated mitochondrial dysfunction, ameliorated the defects in the nucleus morphology, and these cytoprotective effects were accompanied by preserving mitonuclear interaction (including mitonuclear protein imbalance and the mitochondrial unfolded protein response, UPRmt). Furthermore, NAD+-mediated mitonuclear protein imbalance and UPRmt are probably regulated by deacetylase Sirtuin1 (SIRT1). Taken together, our results indicated that NMN pretreatment ameliorated ALI by inducing mitonuclear protein imbalance and activating the UPRmt in an SIRT1-dependent manner.
Keywords: Nicotinamide mononucleotide; acute lung injury; lipopolysaccharide; mitochondria; mitochondrial unfolded protein response.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Cecconi M, Evans L, Levy M, Rhodes A. Sepsis and septic shock. Lancet 2018;392:75–87 - PubMed
-
- Martin CM, Priestap F, Fisher H, Fowler RA, Heyland DK, Keenan SP, Longo CJ, Morrison T, Bentley D, Antman N, STAR Registry Investigators. A prospective, observational registry of patients with severe sepsis: the Canadian sepsis treatment and response registry. Crit Care Med 2009;37:81–8 - PubMed
-
- Bellani G, Laffey JG, Pham T, Fan E, Brochard L, Esteban A, Gattinoni L, van Haren F, Larsson A, McAuley DF, Ranieri M, Rubenfeld G, Thompson BT, Wrigge H, Slutsky AS, Pesenti A. Epidemiology, patterns of care, and mortality for patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome in intensive care units in 50 countries. Jama 2016;315:788–800 - PubMed
-
- Gu J, Luo L, Wang Q, Yan S, Lin J, Li D, Cao B, Mei H, Ying B, Bin L, Smith FG, Jin SW. Maresin 1 attenuates mitochondrial dysfunction through the ALX/cAMP/ROS pathway in the cecal ligation and puncture mouse model and sepsis patients. Lab Invest 2018;98:715–33 - PubMed
-
- Shi J, Yu J, Zhang Y, Wu L, Dong S, Wu L, Wu L, Du S, Zhang Y, Ma D. Pi3k/Akt pathway-mediated HO-1 induction regulates mitochondrial quality control and attenuates endotoxin-induced acute lung injury. Lab Invest 2019;99:1795–809 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

