Tele-Audiology in India: Current and Future Trends in Knowledge, Attitude, and Practice Among Audiologists
- PMID: 35538867
- PMCID: PMC9271733
- DOI: 10.7874/jao.2021.00584
Tele-Audiology in India: Current and Future Trends in Knowledge, Attitude, and Practice Among Audiologists
Abstract
Background and objectives: The COVID-19 pandemic has led to widespread use of telepractice in hearing health care services. In this study, we investigated the knowledge, attitude, and practice (KAP) of tele-audiology among Indian audiologists. The current study is based on tele-practice guidelines recommended by the Indian Speech and Hearing Association for tele-audiology services in India.
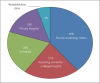
Subjects and methods: An internet-based KAP questionnaire survey was performed among 108 audiologists. The questionnaire included 33 items categorized under the following domains: demographic information and KAP of tele-audiology. Of the 108 audiologists included in the study, 38 admitted to the practice of tele-audiology previously and during the COVID-19 pandemic (tele-practitioners), and 70 respondents had no experience of tele-audiology (non-telepractitioners).
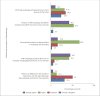
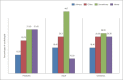
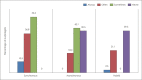
Results: Overall higher scores were observed with regard to the knowledge domain, and a mixed attitude regarding tele-practice was observed among audiologists. Most respondents acknowledged the advantages of tele-audiology in clinical practice. However, audiologists were hesitant to utilize this technology owing to the challenges associated with tele-practice.
Conclusions: Despite adequate awareness and a positive attitude, a gap is observed between available knowledge and its actual application/utilization in tele-audiology. Tele-audiology practice was limited to counseling, hearing impairment treatment, and troubleshooting tips for hearing aids. Evidence-based practices to perform diagnostic test battery in tele-mode, hands-on training to run diagnostic test battery/rehabilitation using a tele-mode approach, and greater understanding of the technical requirements for tele-practice may result in a positive perception and encourage tele-audiology practice among audiologists. Specialized training and regular continuing education programmes are important to promote tele-audiology services in clinical practice.
Keywords: Attitude; Audiologists; Practice; Tele-audiology; Tele-health.
Figures


References
-
- Krumm M. A review of contemporary tele-audiology literature. J Hear Sci. 2016;6:9–21.
-
- Dharmar M, Simon A, Sadorra C, Friedland G, Sherwood J, Morrow H, et al. Reducing loss to follow-up with tele-audiology diagnostic evaluations. Telemed J E Health. 2016;22:159–64. - PubMed
-
- Eikelboom RH, Swanepoel W. International survey of audiologists’ attitudes toward telehealth. Am J Audiol. 2016;25(3S):295–98. - PubMed
-
- Ramkumar V, Selvakumar K, Vanaja CS, Hall JW, Nagarajan R, Neethi J. Parents’ perceptions of tele-audiological testing in a rural hearing screening program in South India. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2016;89:60–6. - PubMed
-
- American Speech-Language-Hearing Association . Survey report on telepractice use among audiologists and speech-language pathologists. Rockville: American Speech-Language-Hearing Association; 2002.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

