Synthesis and characterization of two new mixed-ligand Cu(II) complexes of a tridentate NN'O type Schiff base ligand and N-donor heterocyclic co-ligands: In vitro anticancer assay, DNA/human leukemia/COVID-19 molecular docking studies, and pharmacophore modeling
- PMID: 35538931
- PMCID: PMC9073997
- DOI: 10.1002/aoc.6639
Synthesis and characterization of two new mixed-ligand Cu(II) complexes of a tridentate NN'O type Schiff base ligand and N-donor heterocyclic co-ligands: In vitro anticancer assay, DNA/human leukemia/COVID-19 molecular docking studies, and pharmacophore modeling
Abstract
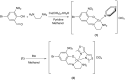
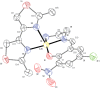
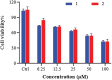
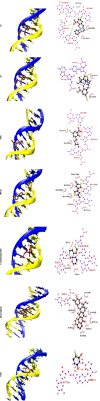
Two new mixed-ligand complexes with general formula [Cu(SB)(L')]ClO4 (1 and 2) were synthesized and characterized by different spectroscopic and analytical techniques including Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) and UV-Vis spectroscopy and elemental analyses. The SB ligand is an unsymmetrical tridentate NN'O type Schiff base ligand that was derived from the condensation of 1,2-ethylenediamine and 5-bromo-2-hydroxy-3-nitrobenzaldehyde. The L' ligand is pyridine in (1) and 2,2'-dimethyl-4,4'-bithiazole (BTZ) in (2). Crystal structure of (2) was also obtained. The two complexes were used as anticancer agents against leukemia cancer cell line HL-60 and showed considerable anticancer activity. The anticancer activity of these complexes was comparable with the standard drug 5-fluorouracil (5-FU). Molecular docking and pharmacophore studies were also performed on DNA (PDB:1BNA) and leukemia inhibitor factor (LIF) (PDB:1EMR) to further investigate the anticancer and anti-COVID activity of these complexes. The molecular docking results against DNA revealed that (1) preferentially binds to the major groove of DNA receptor whereas (2) binds to the minor groove. Complex (2) performed better with 1EMR. The experimental and theoretical results showed good correlation. Molecular docking and pharmacophore studies were also applied to study the interactions between the synthesized complexes and SARS-CoV-2 virus receptor protein (PDB ID:6LU7). The results revealed that complex (2) had better interaction than (1), the free ligands (SB and BTZ), and the standard drug favipiravir.
Keywords: COVID‐19; anticancer; mixed‐ligand; molecular docking; unsymmetrical Schiff base.
© 2022 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Synthesis and crystal structures of new mixed-ligand schiff base complexes containing N-donor heterocyclic co-ligands: Molecular docking and pharmacophore modeling studies on the main proteases of SARS-CoV-2 virus (COVID-19 disease).Polyhedron. 2022 Jul 1;220:115825. doi: 10.1016/j.poly.2022.115825. Epub 2022 Apr 4. Polyhedron. 2022. PMID: 35399322 Free PMC article.
-
New platinum (II) complexes based on schiff bases: synthesis, specification, X-ray structure, ADMET, DFT, molecular docking, and anticancer activity against breast cancer.J Biol Inorg Chem. 2023 Aug;28(5):519-529. doi: 10.1007/s00775-023-02005-1. Epub 2023 Jul 15. J Biol Inorg Chem. 2023. PMID: 37452868
-
Bio-active mixed ligand Cu(II) and Zn(II) complexes of pyrimidine derivative Schiff base: DFT calculation, antimicrobial, antioxidant, DNA binding, anticancer and molecular docking studies.J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2021 May;39(8):3012-3024. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2020.1759454. Epub 2020 May 5. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2021. PMID: 32329409
-
Synthesis, Characterization, DFT Studies of Novel Cu(II), Zn(II), VO(II), Cr(III), and La(III) Chloro-Substituted Schiff Base Complexes: Aspects of Its Antimicrobial, Antioxidant, Anti-Inflammatory, and Photodegradation of Methylene Blue.Molecules. 2023 Jun 15;28(12):4777. doi: 10.3390/molecules28124777. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37375332 Free PMC article.
-
Structural features and antiproliferative activity of Pd(II) complexes with halogenated ligands: a comparative study between Schiff base and reduced Schiff base complexes.Dalton Trans. 2024 Jun 25;53(25):10571-10591. doi: 10.1039/d4dt00132j. Dalton Trans. 2024. PMID: 38855858
Cited by
-
Development of Metal Complexes for Treatment of Coronaviruses.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jun 8;23(12):6418. doi: 10.3390/ijms23126418. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35742870 Free PMC article.
-
Unusual Ni⋯Ni interaction in Ni(ii) complexes as potential inhibitors for the development of new anti-SARS-CoV-2 Omicron drugs.RSC Med Chem. 2024 Feb 20;15(3):895-915. doi: 10.1039/d3md00601h. eCollection 2024 Mar 20. RSC Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 38516589 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zehra S., Roisnel T., Arjmand F., ACS Omega 2019, 4, 7691. 10.1021/acsomega.9b00131 - DOI
-
- Salihović M., Pazalja M., Špirtović Halilović S., Veljović E., Mahmutović‐Dizdarević I., Roca S., Novaković I., Trifunović S., J. Mol. Struct. 2021, 1241, 130670. 10.1016/j.molstruc.2021.130670 - DOI
-
- Liu M., Yang H., Li D., Yao Q., Wang H., Zhang Z., Dou J., Inorg. Chim. Acta 2021, 522, 120384. 10.1016/j.ica.2021.120384 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
