Lipidomic characterisation discovery for coronary heart disease diagnosis based on high-throughput ultra-performance liquid chromatography and mass spectrometry
- PMID: 35538954
- PMCID: PMC9076928
- DOI: 10.1039/c7ra09353e
Lipidomic characterisation discovery for coronary heart disease diagnosis based on high-throughput ultra-performance liquid chromatography and mass spectrometry
Abstract
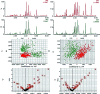
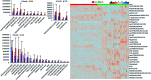
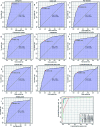
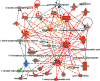
Although many diagnostic tools have been developed for coronary heart disease (CHD), its diagnosis is still challenging. Lipids play an important role in diseases and a lipidomics approach could offer a platform to clarify the pathogenesis and pathologic changes of this disease. To the best of our knowledge, no lipidomics studies on serum have been attempted to improve the diagnosis and identify the potential biomarkers of CHD. The aim of this study was to investigate the distinctive lipid changes in serum samples of CHD patients and to identify candidate biomarkers for the reliable diagnosis of CHD using this platform. In this study, the serum lipid profiles of CHD patients were measured via ultra-performance liquid chromatography-G2-Si-high definition mass spectrometry combined with multivariate data analysis. A MetaboAnalyst tool was used for the analysis of the receiver operating-characteristic, while the IPA software was applied for the pathway analysis. The obtained results inferred that 33 lipid molecular species involving 6 fatty acids, 21 glycerophospholipids and 6 sphingolipids have significant differences in the serum of CHD patients. Simultaneously, 4 upstream regulatory proteins related to lipid metabolism disorders of CHD were predicted. Ten lipids have high clinical diagnostic significance according to the receiver operating-characteristic curves. This research shows that the in-depth study of lipids in the serum contributes to the clinical diagnosis of CHD and interprets the occurrence and development of CHD.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no financial interest in relation to the publication of this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Screening of lipid metabolism biomarkers in patients with coronary heart disease via ultra-performance liquid chromatography-high resolution mass spectrometry.J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2021 Apr 15;1169:122603. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2021.122603. Epub 2021 Feb 23. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 33690078
-
Exploring lipid biomarkers of coronary heart disease for elucidating the biological effects of gelanxinning capsule by lipidomics method based on LC-MS.Biomed Chromatogr. 2021 Jul;35(7):e5091. doi: 10.1002/bmc.5091. Epub 2021 Mar 8. Biomed Chromatogr. 2021. PMID: 33618435
-
An Unbiased Lipid Phenotyping Approach To Study the Genetic Determinants of Lipids and Their Association with Coronary Heart Disease Risk Factors.J Proteome Res. 2019 Jun 7;18(6):2397-2410. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.8b00786. Epub 2019 Apr 26. J Proteome Res. 2019. PMID: 30887811 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in lipidomics.Clin Chim Acta. 2020 Nov;510:123-141. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2020.06.049. Epub 2020 Jul 3. Clin Chim Acta. 2020. PMID: 32622966 Review.
-
Ultra-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry as a sensitive and powerful technology in lipidomic applications.Chem Biol Interact. 2014 Sep 5;220:181-92. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2014.06.029. Epub 2014 Jul 9. Chem Biol Interact. 2014. PMID: 25014415 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting regulation of tryptophan metabolism for colorectal cancer therapy: a systematic review.RSC Adv. 2019 Jan 23;9(6):3072-3080. doi: 10.1039/c8ra08520j. eCollection 2019 Jan 22. RSC Adv. 2019. PMID: 35518968 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipid alterations in acute myocardial infarction are associated with gut microbiota.Microbiol Spectr. 2025 Apr;13(4):e0237024. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.02370-24. Epub 2025 Feb 19. Microbiol Spectr. 2025. PMID: 39969201 Free PMC article.
-
High-throughput lipidomics reveal mirabilite regulating lipid metabolism as anticancer therapeutics.RSC Adv. 2018 Oct 18;8(62):35600-35610. doi: 10.1039/c8ra06190d. eCollection 2018 Oct 15. RSC Adv. 2018. PMID: 35547938 Free PMC article.
-
A high-throughput and untargeted lipidomics approach reveals new mechanistic insight and the effects of salvianolic acid B on the metabolic profiles in coronary heart disease rats using ultra-performance liquid chromatography with mass spectrometry.RSC Adv. 2020 May 1;10(29):17101-17113. doi: 10.1039/d0ra00049c. eCollection 2020 Apr 29. RSC Adv. 2020. PMID: 35521479 Free PMC article.
-
Chinmedomics: a potent tool for the evaluation of traditional Chinese medicine efficacy and identification of its active components.Chin Med. 2024 Mar 13;19(1):47. doi: 10.1186/s13020-024-00917-x. Chin Med. 2024. PMID: 38481256 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Yang S. Shen H. Rong Z. Hong L. Coronary atherosclerosis prediction based on carotid and femoral atherosclerosis. Shanghai Medical Imaging. 2005;14(2):129–130.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

