Palladium/phosphorus-functionalized porous organic polymer with tunable surface wettability for water-mediated Suzuki-Miyaura coupling reaction
- PMID: 35539056
- PMCID: PMC9075338
- DOI: 10.1039/c9ra06680b
Palladium/phosphorus-functionalized porous organic polymer with tunable surface wettability for water-mediated Suzuki-Miyaura coupling reaction
Abstract
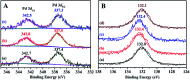
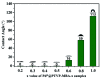
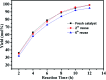
A series of phosphorus-functionalized porous organic polymers supported palladium catalysts with tunable surface wettability were successfully prepared using an easy copolymerization and successive immobilization method. The obtained polymers were carefully characterized by many physicochemical methods. Characterization results suggested that the prepared materials featured hierarchically porous structures, high pore volumes, tunable surface wettability and strong electron-donating ability towards palladium species. We demonstrated the use of these solid catalysts for water-mediated Suzuki-Miyaura coupling reactions. It was found that the surface wettability of the prepared catalysts has an important influence on their catalytic activities. The optimal catalyst, which has excellent amphipathicity and relatively high phosphorus concentration, displayed superior catalytic activity compared to the other catalysts. Under ambient conditions, a variety of aryl chlorides can be efficiently transformed to biaryls in high yields. Moreover, the catalyst could be easily recovered and reused at least six times.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures




References
-
- Kitanosono T. Masuda K. Xu P. Kobayashi S. Chem. Rev. 2018;118:679–746. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.7b00417. - DOI - PubMed
- Nasseri M. A. Alavi S. A. Kazemnejadi M. Allahresani A. RSC Adv. 2019;9:20749–20759. doi: 10.1039/C9RA03406D. - DOI
- Dong Y. Chen Y. Q. Jv J. J. Li Y. Li W. H. Dong Y. B. RSC Adv. 2019;9:21671–21678. doi: 10.1039/C9RA04103F. - DOI
-
- Breslow R., A Fifty-Year Perspective on Chemistry in Water, in Organic Reactions in Water, ed. U. M. Lindström, Blackwell, Oxford, UK, 2007, pp. 1–28
- Chen Z. and Ren H., The Applications of Water as Reagents in Organic Synthesis, in Solvents as Reagents in Organic Synthesis, ed. X.-F. Wu, Wiley-VCH, New York, 2017, pp. 1–44
-
- Xu H. Gao J. Jiang D. Nat. Chem. 2015;7:905. doi: 10.1038/nchem.2352. - DOI - PubMed
- Das S. Heasman P. Ben T. Qiu S. Chem. Rev. 2016;117:1515–1563. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.6b00439. - DOI - PubMed
- Wang C. A. Nie K. Song G. D. Li Y. W. Han Y. F. RSC Adv. 2019;9:8239–8245. doi: 10.1039/C9RA00460B. - DOI
- Dong Y. Jv J. J. Li Y. Li W. H. Chen Y. Q. Sun Q. Ma J. P. Dong Y. B. RSC Adv. 2019;9:20266–20272. doi: 10.1039/C9RA03679B. - DOI
-
- Hartwig J. F., Organotransition Metal Chemistry: From Bonding to Catalysis, University Science Books, Sausalito, 2010, pp. 33–41
- Guan Z. Li B. Hai G. Yang X. Li T. Tan B. RSC Adv. 2014;4:36437–36443. doi: 10.1039/C4RA06551D. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

